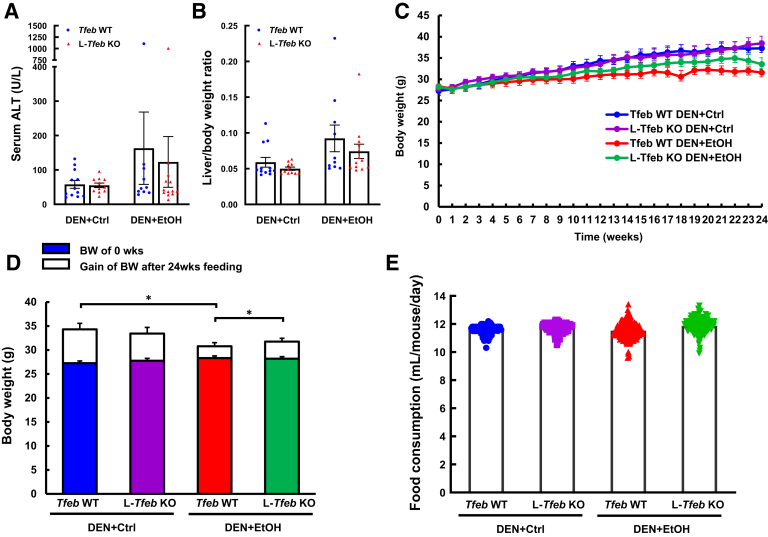
Figure 2.
Chronic ethanol (EtOH) feeding increases liver injury and hepatomegaly, and reduces body weight gain in diethylnitrosamine (DEN)–treated mouse livers. Male Tfeb wild-type (WT) and L-Tfeb knockout (KO) mice were treated with a DEN-alcohol–associated hepatocellular carcinoma model. Serum alanine aminotransferase (ALT) activity (A) and liver/body weight (BW) ratio (B) were measured. Mouse body weight was monitored weekly (C and D), and volume of liquid food consumption was recorded daily (E). Data are presented as means ± SEM (A–E). n = 10 to 13 (A–E). ∗P < 0.05 (one-way analysis of variance with Bonferroni post hoc test). Ctrl, control.