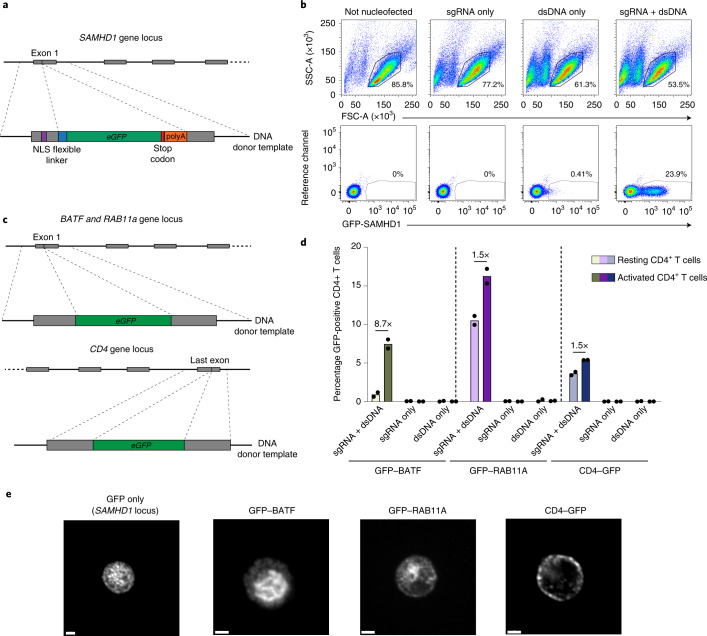
Fig. 4. CRISPR-Cas9-mediated knock in of eGFP into different loci in resting CD4+ T cells.
a, KI-targeting strategy to introduce eGFP into the SAMHD1 locus. b, Cell viability and GFP expression after KI of the dsDNA cassette shown in a. Cells nucleofected with sgRNA2 only or with dsDNA only served as references. One representative experiment is shown (n = 3). c, KI-targeting strategy to introduce GFP to the N terminus of either BATF or RAB11A, or to the C terminus of CD4, in principle as reported for activated T cells30. d, GFP expression after KI of constructs from c analyzed by flow cytometry (sgRNA + dsDNA). Nucleofection of sgRNA only or dsDNA only served as references. CD4+ T cells were kept either resting or activated 3 d after nucleofection. Means of two independent donors are shown. e, Activated KI CD4+ T cells shown in d were fixed and stained with an antibody against GFP and analyzed by confocal microscopy. Representative micrographs from one experiment are shown (n = 3). Scale bars, 2 µm.