Figure 1. Bioallethrin elicits spatial repellency in Ae. aegypti mosquitoes.
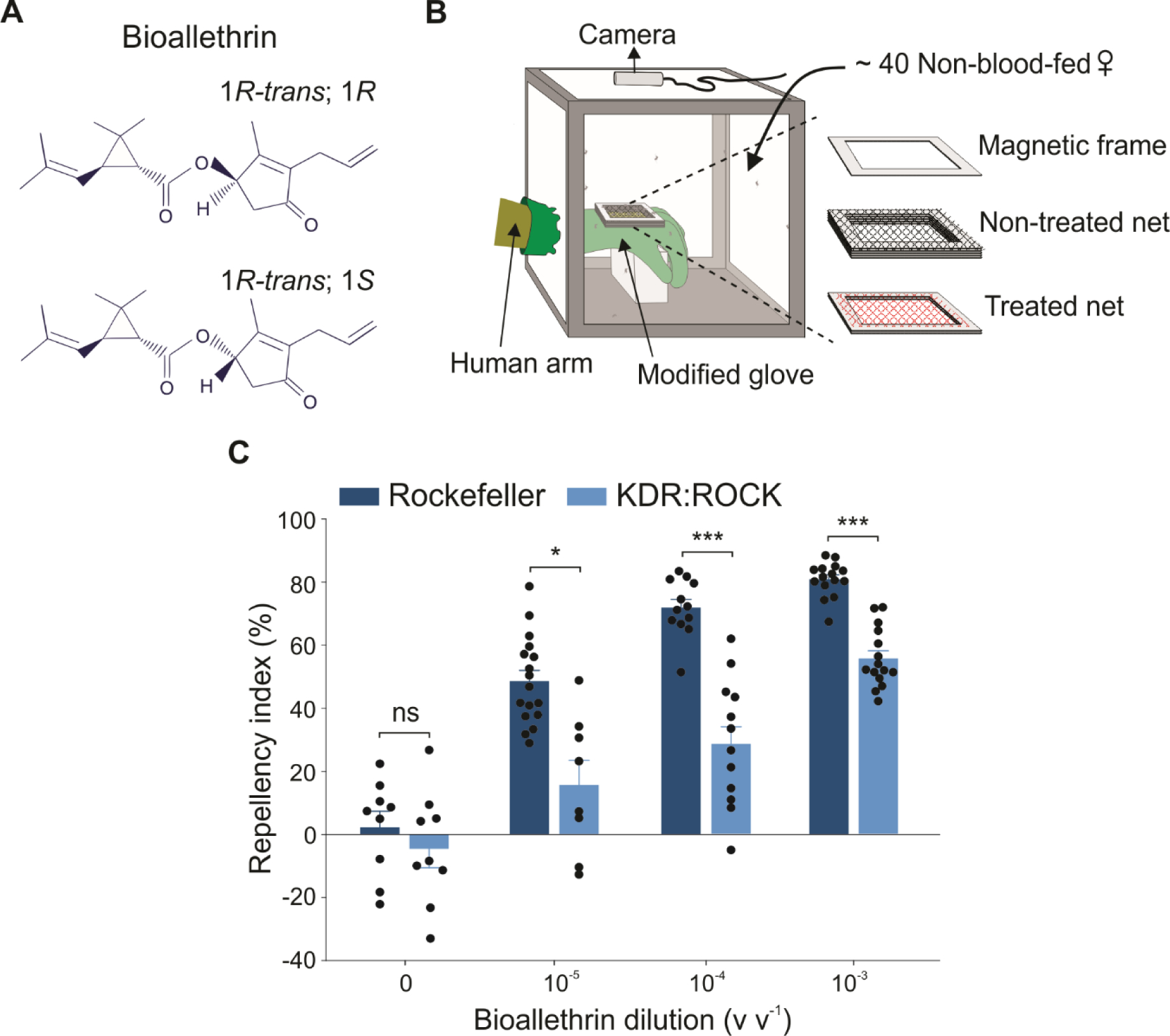
(A) Chemical structure of bioallethrin. Bioallethrin (or d-trans allethrin) is a mixture of two allethrin isomers (i.e., 1R-trans; 1R and 1R-trans; 1S). (B) A schematic drawing illustrating the hand-in-cage setup used to evaluate spatial repellency. (C) Concentration-dependent bioallethrin repellency in Rockefeller (wild-type) and KDR:ROCK (pyrethroid-resistant) mosquitoes. Two-tailed Student’s t-test, control (0): t = 0.212, df = 8, P = 0.837; 10−5 dilution: t = 3.024, df = 8, P = 0.016, 10−4 dilution: t = 6.171, df = 11, P < 0.0001; 10−3 dilution: t = 8.552, df = 14, P < 0.0001; ns = not significant; *P < 0.05, ***P < 0.001; n = 10 cages for Rockefeller and 9 for KDR:ROCK in control (0), n = 17 cages for Rockefeller and 9 cages for KDR:ROCK in 10−5 dilution, n = 12 cages for Rockefeller and 13 cages for KDR:ROCK in 10−4 dilution, and n = 15 cages for both Rockefeller and KDR:ROCK in 10−3 dilution. The 10−5, 10−4, and 10−3 dilutions correspond to 0.114, 1.14, and 11.4 μg cm−2, respectively. The control represents the baseline activity in response to the solvent. Data are presented as mean ± SEM. The dots over bars represent individual replicate values. Experiments were conducted independently by two additional researchers.
