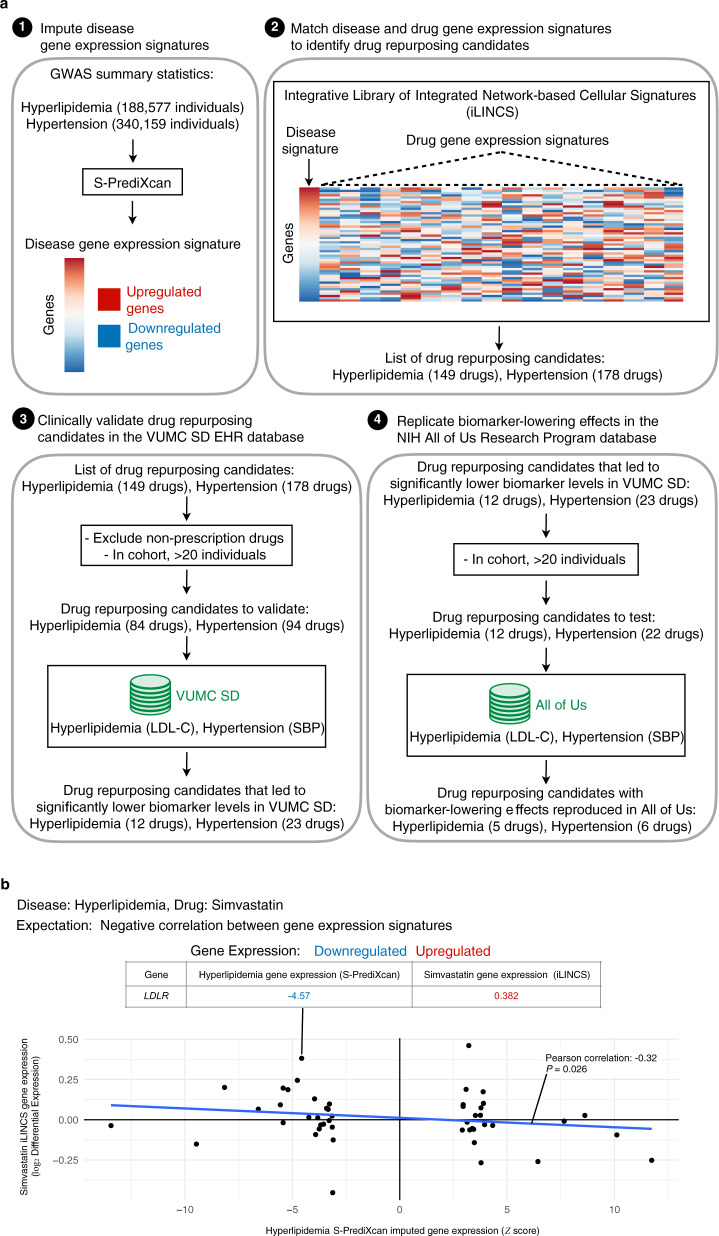
Fig. 1. Study design and workflow.
a (1) For each disease, disease-associated gene expression changes were imputed using each disease’s GWAS summary statistics and S-PrediXcan. Using the list of imputed disease-associated gene expression changes, the top up- and downregulated genes were used to compute a disease gene expression signature. (2) The disease gene expression signature was then uploaded to the drug perturbation platform, iLINCS. From iLINCS, an initial list of drug repurposing candidates was obtained; drugs in this list induced perturbations that reversed the disease gene expression signature (see b). (3) A subset of the iLINCS drug repurposing candidates was clinically validated in the VUMC SD EHR database (Fig. 2). (4) Drugs with significant biomarker-lowering effects in the VUMC SD were chosen for replication studies in the NIH All of Us Research Program database. b Example of disease and drug-gene expression signature matching (second step in a). Each point represents one gene. Since simvastatin is a known lipid-lowering drug, the simvastatin induced gene expression signature was predicted to reverse the S-PrediXcan imputed gene expression signature for hyperlipidemia, i.e., the signatures were expected to have an inverse relationship. This inverse relationship is indicated by the blue line, which shows a negative correlation (Pearson correlation coefficient and two-tailed test P-value) between the S-PrediXcan imputed gene expression signature for hyperlipidemia (horizontal axis) and the iLINCS gene expression signature for simvastatin (vertical axis). As expected, the LDLR gene was downregulated in individuals with hyperlipidemia and upregulated in simvastatin perturbation experiments. GWAS genome-wide association study, iLINCS Integrative Library of Integrated Network-based Cellular Signatures, EHR electronic health record, LDL-C low-density lipoprotein cholesterol, SBP systolic blood pressure, VUMC Vanderbilt University Medical Center, SD Synthetic Derivative, NIH National Institutes of Health.