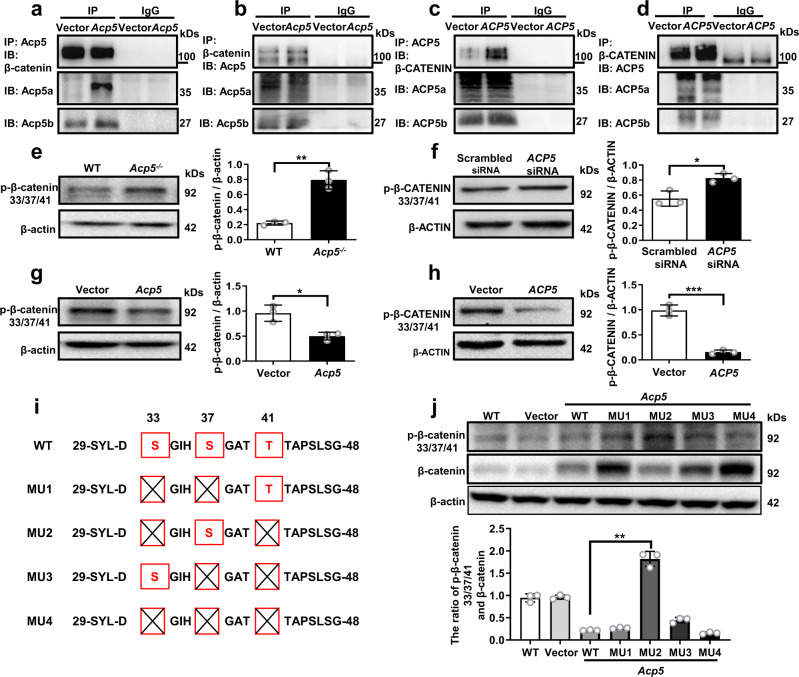
Fig. 5. Acp5 dephosphorylates β-catenin at Ser33 and Thr41.
a–d Coimmunoprecipitation of Acp5 and β-catenin in PMLFs (a, b) and in PHMLs (c, d). e–h Western blot analysis of the levels of p-β-catenin (S33, S37 and T41) in WT and Acp5−/− PMLFs (e, p = 0.0013), ACP5 siRNA and Scrambled siRNA treated PHLFs (f, p = 0.0159), Acp5-plasmid and Vector treated Acp5−/− PMLFs (g, p = 0.0188) and Acp5-plasmid and Vector treated PHLFs (h, p = 0.0003). i The schematic results showing the mutant plasmids (MU1-3) of these three phosphorylated sites. Each of mutant plasmids (MU1-3) of these three phosphorylated sites maintained one normal site and two mutant sites (red boxes), and all phosphorylated sites were deleted in MU4. j Western blot analysis of the levels of β-catenin and p-β-catenin (S33, S37 and T41) in PMLFs following plasmids transduced (p = 0.0036). The data are represented as the mean ± SEM of three independent experiments. Two-sided Student’s t-test (a–i) and two-sided unpaired Student’s t-test with Welch’s correction (j) were applied. *p < 0.05; **p < 0.01; ***p < 0.001. Source data are provided as a Source Data file.