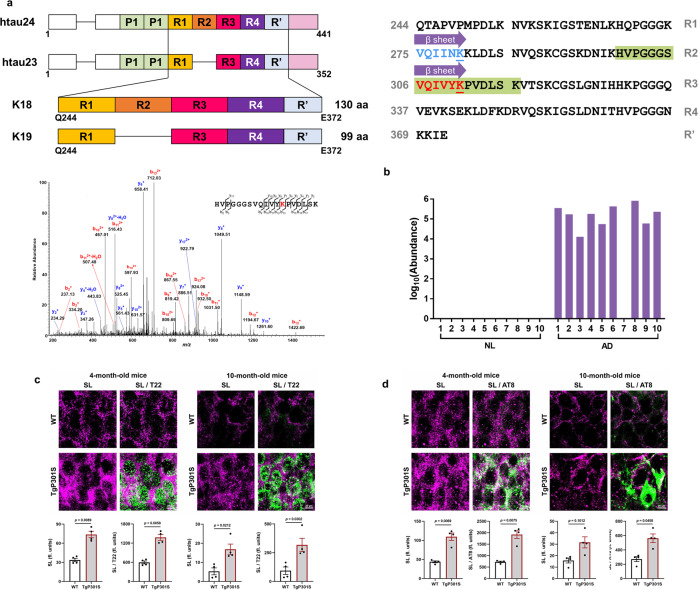
Fig. 6. The unique succinylation of K311 on tau in brains from patients with AD.
a Domain structure of tau and the location of succinylation K311. The diagram shows the domain structure of htau23 and 24, which contain three and four repeats, respectively. The constructs K18 and K19 comprise four repeats and three repeats, respectively. Residues are numbered according to tau441 sequence. Purple arrow represents the two central strands of the β-sheet (PHF6*: Val275-Lys280, highlighted in blue, the blue underlined lysine refers to acetylated K280; PHF6: Val306-Lys311, highlighted in red, the red underlined lysine refers to succinylated K311). Green highlights the peptide identified by MS. MS2 spectrum of m/z 694.04073+ leads to confident identification of a succinylated peptide from tau protein with K311 succinylation site being highlighted in red text. b Abundance of succinylation K311 found in brains from ten controls and ten patients with AD. Data transformed by log10 (abundance) for normalization purposes and to facilitate presentation. c High-resolution images acquired using confocal laser microscopy display the colocalization of succinylation(magenta) and tau oligomers(green) in the hippocampus of 4-month-old and 10-month-old Tg19959 or WT mice (n = 4 per each group, two-tailed Student’s t-tests). d Fluorescence micrographs obtained from the hippocampus of 4-month-old and 10-month-old Tg19959 or WT mice show the colocalization between succinylation(magenta) and NFTs (green) (n = 4 per each group, two-tailed Student’s t-tests). Source data are provided as a Source Data file.