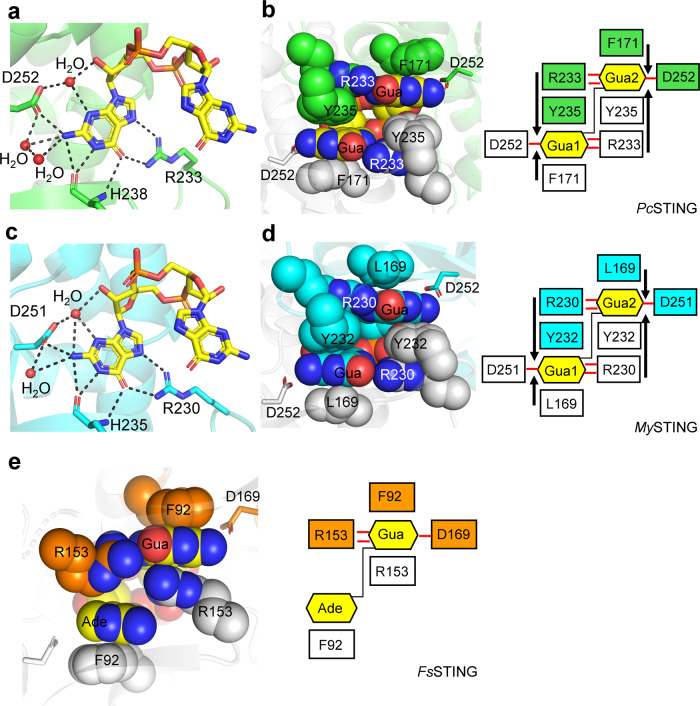
Fig. 2. Recognition of c-di-GMP by PcSTING/MySTING and 3’3’-cGAMP by FsSTING.
a, c Enlarged view of the ligand-binding pocket of (a) PcSTING (green) and (c) MySTING (cyan). The hydrogen-bonding network that specifically recognizes the guanine nucleobase of c-di-GMP (yellow) are indicated by a black dashed line. The specificity-determining residues of PcSTING, MySTING, and c-di-GMP molecule are shown as sticks. Water molecules are shown as red spheres. b, d Left, the four-layer stacking interactions between c-di-GMP and (b) PcSTING dimer (green and light gray) and (d) MySTING dimer (cyan and light gray); right, schematic representation of the interactions. C-di-GMP and the residues involved in stacking (F171, R233, Y235 in PcSTING; L169, R230, Y232 in MySTING) are shown as spheres. One protomer is colored and the other is white. D252/D251 in PcSTING/MySTING that recognizes N2 of guanine base is shown as sticks. The four-layer stack binding mode is highlighted by black arrows. The H-bonds are indicated by red lines. e Left, the stacking interactions between 3’3’-cGAMP (yellow) and FsSTING dimer (orange and light gray, PDB: 6WT4); right, schematic representation of the interactions. 3’3’-cGAMP and the residues involved in stacking (F92 and R153 in FsSTING) are shown as spheres. D169s in FsSTING are shown as sticks. Gua, guanine base; Ade, adenine base.