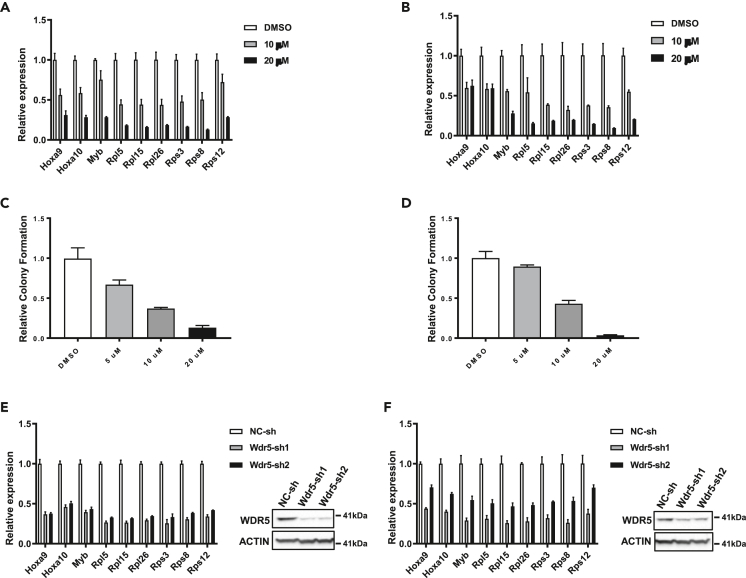
Figure 7.
Setbp1- and Setbp1(D/N)-induced AML cells are sensitive to WDR5 inhibition
(A) Real-time RT-PCR analysis of indicated SETBP1/MLL1 co-bound targets in Setbp1-induced AML cells at 72 h after treatment with OICR-9429 at indicated concentration or control DMSO. Data are represented as mean ± SD (n = 3).
(B) Real-time RT-PCR analysis of same genes in Setbp1(D/N)-induced AML cells at 72 h after treatment with OICR-9429 or control DMSO. Data are represented as mean ± SD (n = 3).
(C) Relative colony formation by Setbp1-induced AML cells upon treatment with WDR5 inhibitor OICR-9429 at indicated concentration or control DMSO. Data are represented as mean ± SD (n = 3).
(D) Relative colony formation by Setbp1(D/N)-induced AML cells upon treatment with WDR5 inhibitor OICR-9429 at indicated concentration or control DMSO. Data are represented as mean ± SD (n = 3).
(E) Left panel, real-time RT-PCR analysis of relative indicated SETBP1/MLL1 co-bound targets in Setbp1-induced AML cells after transduction with Wdr5-specific shRNAs (Wdr5-sh1 and -sh2) or a non-targeting control shRNA (NC-sh). Data are represented as mean ± SD (n = 3). Right panel, western blotting analysis of the same transduced cells using indicated antibodies.
(F) Same analyses as in (E) for Setbp1(D/N)-induced AML cells.