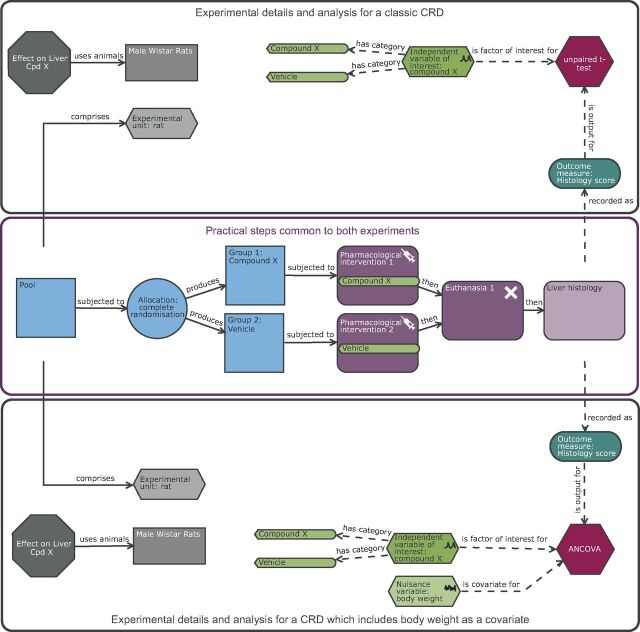
Figure 2.
Schematic of a completely randomised design (CRD) of a rat liver study exploring the effect of compound X on the histological score either as a classic experiment or as an experiment which includes a covariate. The purple section highlights the common practical steps: In a complete randomised design experiment, there is one factor of interest, and in this scenario it is treatment which has two possible levels (vehicle or compound X). The animals are the experimental units and form a pool which are randomly allocated to the two treatment groups prior to exposure. In this design, the male Wistar rat is the biological unit, experimental unit and observation unit. The upper black section details the experimental and analysis details for a classic CRD while the lower black section details the CRD with a covariate of pre-treatment body weight and hence includes in the analysis the nuisance variable body weight. The inclusion of the pre-treatment body weight will increase the power if body weight is correlated to the outcome measure. The inclusion subtly impacts the conclusion in that the estimated treatment effect would be the change in means after adjusting for any differences in pre-treatment body weight.