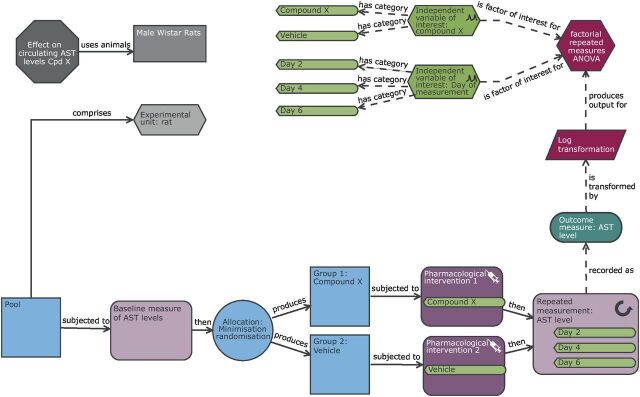
Figure 7.
Schematic of a repeat measure design to study the effect of compound X on the circulating aspartate transaminase (AST) levels with time. In comparison with the original completely randomised design (figure 2), the outcome measure here is circulating AST levels which is monitored over multiple days. As this design is interested in how these levels change following exposure, there is a repeated measurement node in the design indicating that the readings are taken on days 2, 4 and 6. Furthermore, within the practical steps, we can see a baseline measure of AST level is taken prior to exposure and this is used in the allocation process to minimise potential differences in this variable at the group level. The AST variable has an underlying log normal transformation; consequently in the analysis section of the diagram, there is a transformation node to highlight the log10 transformation necessary to meet the statistical analysis assumptions of normality. In this design, the experimental unit, observation unit and biological unit is the rat and the experiment will be testing the hypotheses of whether the AST level depends on compound exposure, the day of measurement and whether the effect of compound varies with time (day 2 to day 6).