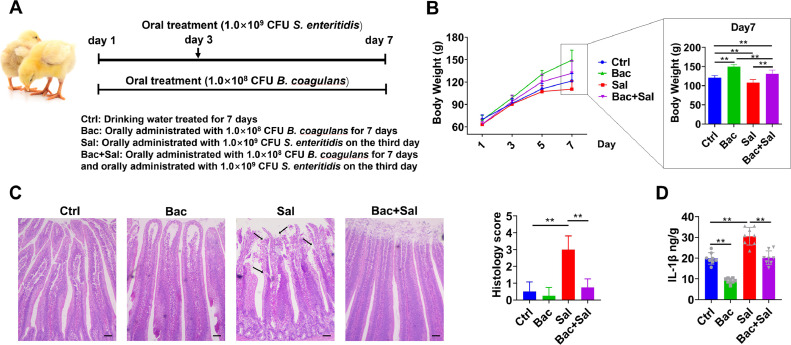
Figure 2.
.B. coagulans ameliorates S. enteritidis-induced intestinal mucosal damage in chicks. (A) Newborn chicks were administrated with drinking water or B. coagulans (1.0 × 108 CFU/mL) suspended in drinking water once a day, for a period of 7 d. Chicks were orally administered with S. enteritidis (1.0 × 109 CFU/mL) on the third day. On the 7th day, chicks were sacrificed for subsequent experiments. (B) The body weight changes of chicks were monitored every 2 d; n = 15 per group. (C) Histopathological changes in jejunum tissues were examined by HE staining, and scoring was performed as described in the Materials and Methods (scale bar =50 μm). The areas marked by the arrows were the exfoliation of intestinal epithelial cells caused by S. enteritidis; n = 6 per group. (D) The concentration of IL-β in jejunum tissues was detected using an ELISA kit; n = 8 per group. Data are presented as the mean ± SDs. *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01.