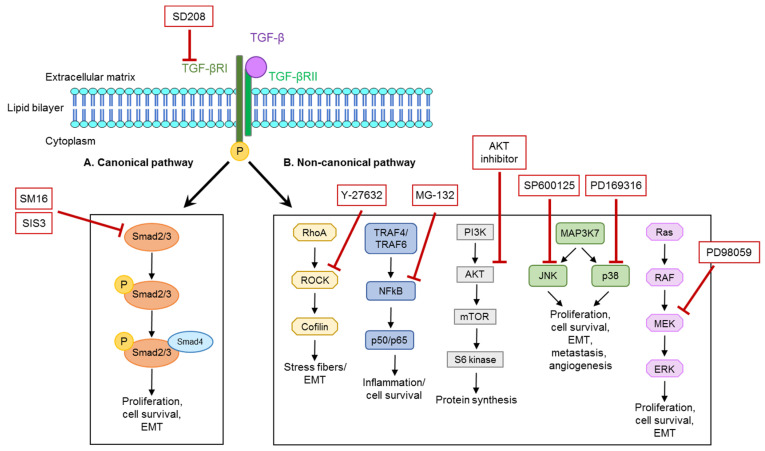
Figure 1.
Illustration of canonical and non-canonical TGF-β pathways and the respective inhibitors used for the blockade of separate parts of the pathways. TGF-β signaling is intracellularly mediated via a canonical, SMAD2- and SMAD3-dependent pathway or different non-canonical pathways, which signal via different routes, namely the Rho-ROCK, NFkB, PI3K-AKT-mTOR, and MAP-kinase pathways via JNK or p53 and Ras-Raf-MEK-ERK. Each signaling arm facilitates different reactions in the cell, such as proliferation, cell survival, epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition (EMT), or protein synthesis (adapted from [18]).