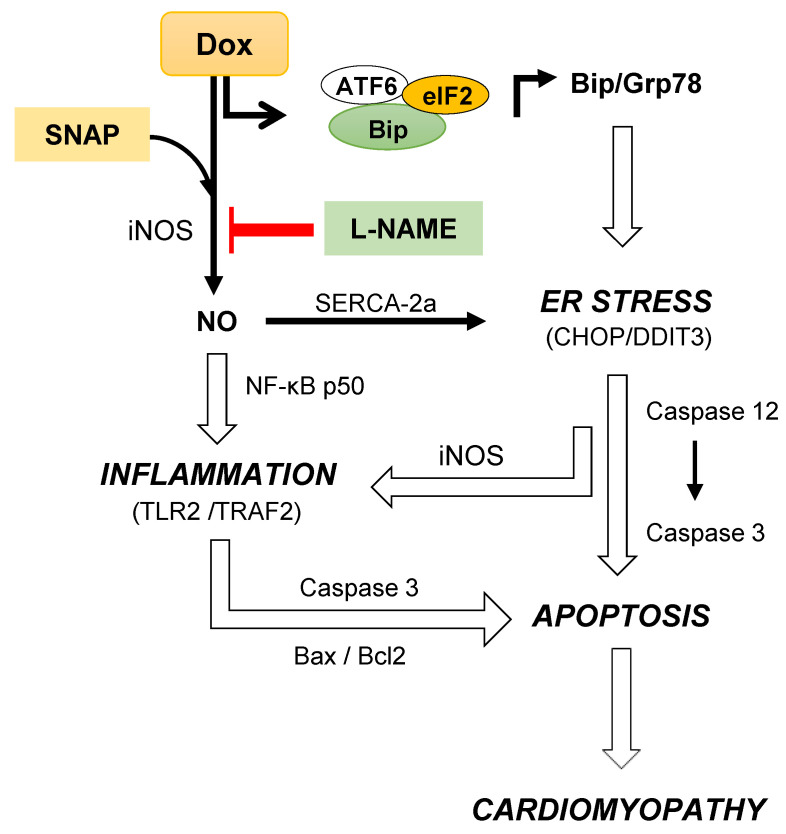
Figure 6.
Dox -induced synergistic inflammatory and ER stress responses leading to apoptosis and cardiomyopathy: Dox dissociates Bip from the Bip-ATF6-eIF2α complex suggested to cause an ER stress and increase in UPR signaling [20]. Such an adaptive response induces iNOS and TLR2 activation following through the regulation of NF-κB p50 and as a result enhancing inflammation. Dox-induced iNOS activation also increases NO and triggers nitrosative stress in isolated cardiomyocytes and in the heart [6,7]. As reported earlier, it is evident that NO donor increases iNOS activity and Dox paradoxically inhibited NO-induced iNOS without change in eNOS activity. Increased iNOS-mediated TLR2 activation results in an ER-induced apoptosis and cardiomyopathy via CHOP/DDIT3 and intrinsic Caspase 3 activation. NOS inhibitor L-NAME may mitigate such Dox-induced ER stress-mediated inflammation, apoptosis and ultimately cardiomyopathy.