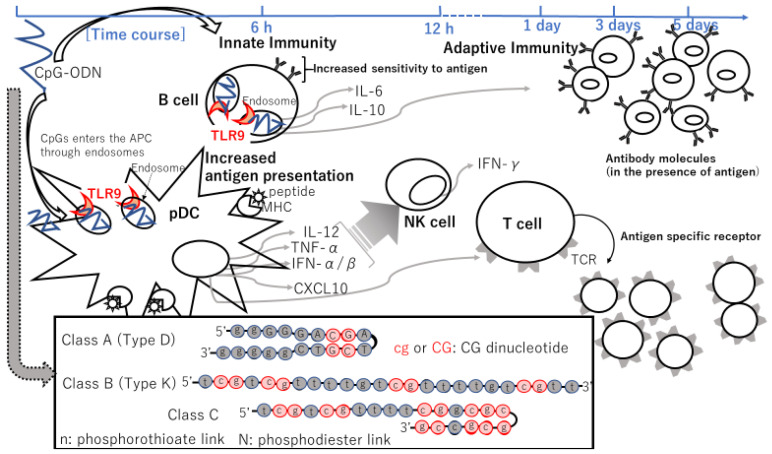
Figure 3.
CpG-ODN cellular mechanism of action. DNA containing one or more CpG motifs is taken up by endocytosis in most cell types, but only activates cells expressing the TLR9 receptor (B cells and pDC in humans). These cells create a TH1-like cytokine milieu by secreting IFN-α/β, IL-12, CXCL10, and other Th1-promoting cytokines and chemokines. NK cells are secondarily activated, secreting IFN-γ and gaining lytic activity. In addition, B cells become more sensitive to activation through their antigen receptors, and both B cells and pDCs have enhanced expression of costimulatory molecules, improving their ability to activate T-cell responses. Class A (also called Type D) ODNs have a phosphodiester core flanked by phosphorothioate terminal nucleotides (in box). They carry a single CpG (indicated in red circles) motif flanked by a palindromic sequence that enables the formation of a stem-loop structure. Class A ODN also possesses poly G motifs at the 3′ and 5′ ends that promote concatamer formation. Class A ODNs initiate pDC to mature and secrete IFN-α but have no effect on B cells. Class A ODNs are kept for longer periods in the early endosome. Class B (also referred to as Type K) ODNs contain 1–5 CpG motifs (in red circles) typically on a phosphorothioate backbone. Class B ODNs trigger pDC to differentiate and produce TNF-α and stimulate B cells to proliferate and secrete IgM. Class B ODNs are rapidly transported through early endosomes into late endosomes. This backbone augments resistance to nuclease digestion. Class C ODNs resemble Class B ODNs in being comprised completely of phosphorothioate nucleotides but are similar to Class A ODNs in including palindromic CpG motifs that can form stem-loop conformation or dimers. Class C ODNs provoke B cells to produce IL-6 and pDCs to secrete IFN-α. Class C ODNs keep activity in both early and late endosomes, and therefore have characteristics in common with both Class A and Class B ODNs. APC, antigen-presenting cell; CpG-ODNs, CpG oligodeoxynucleotides; CXCL10, C-X-C motif chemokine ligand 10; IP-10, IFN-gamma-inducible protein of 10 kilodalton; pDCs, plasmacytoid dendritic cells; MHC, major histocompatibility complex; NK, natural killer; TCR, T-cell receptor; TLR9, Toll-like receptor 9.