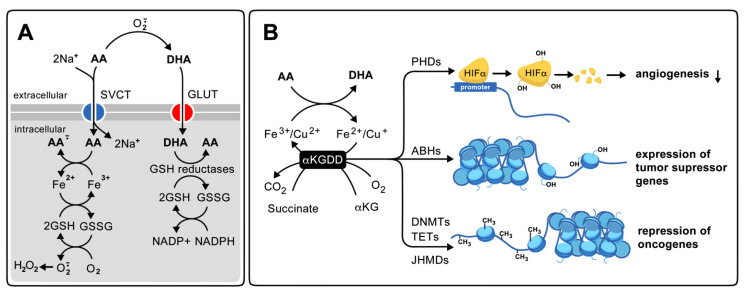
Figure 3.
Proposed mechanisms of anti-cancer action of high doses of vitamin C. (A): Pro-oxidant; (B) regulator of gene expression. DHA: dehydroascorbic acid, AA: ascorbic acid, SVCT: sodium-vitamin c transporter, GLUT: glucose transporter, GSH: reduced glutathione, GSSG: oxidized glutathione, NADP: oxidized nicotinamide dinucleotide phosphate, NADPH: reduced nicotinamide dinucleotide phosphate, αKGDD: α-ketoglutarate-dependent Fe2+ dioxygenase enzymes, αKG: α-ketoglutarate, PHD: hypoxia inducible transcription factor alpha prolyl hydroxylases, HIF α: hypoxia inducible transcription factor alpha, ABH: histone Alpha/Beta hydrolase, DNMTs: DNA methytransferases, TET: ten-eleven translocases DNA demethylases, JHMDs: histone demethylases with Jumonji domain. Translated and modified from Villagran et al. [9].