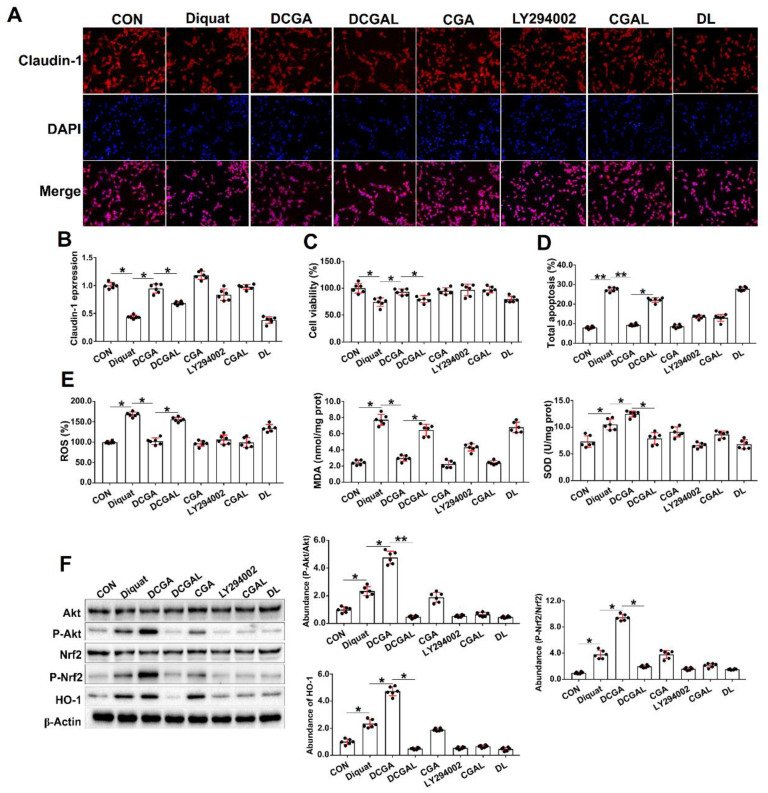
Figure 3.
Chlorogenic acid (CGA) attenuates oxidative stress-induced injury in IPEC-J2 cells via phosphatidylinositol-3-kinase (PI3K)/protein kinase B (Akt) signaling. (A) Localization of the tight-junction protein claudin-1 by immunofluorescence staining. IPEC-J2 cells were plated in 24-well plates at a density of 1 × 105 cells/well (n = 6). (B) qPCR analysis of the expression levels of claudin-1. (C) Assays of cell viability. (D) Analysis of cell apoptosis by flow cytometric assays. (E) Intracellular contents of oxygen reactive species (ROS), malondialdehyde (MDA), and superoxide dismutase (SOD). (F) Western-blot analysis of critical signaling proteins involved in the PI3K/Akt pathway. CON, cells without being treated; Diquat, cells were only treated by 100 µM diquat; CGA, cells were only treated by 100 µM CGA; DCGA, cells were pretreated by 100 µM CGA for 6 h and were then treated by 100 µM diquat for 3 h. DCGAL, cells were pretreated by 10 µM LY294002 for 1 h and were then treated by 100 µM CGA and 100 µM diquat; LY294002, cells were only treated by 10 µM LY294002; CGAL, cells were pretreated by 10 µM LY294002 for 1 h and were then treated by 100 µM CGA; DL, cells were pretreated by 10 µM LY294002 for 1 h and were then treated by 100 µM diquat. * p < 0.05, ** p < 0.01.