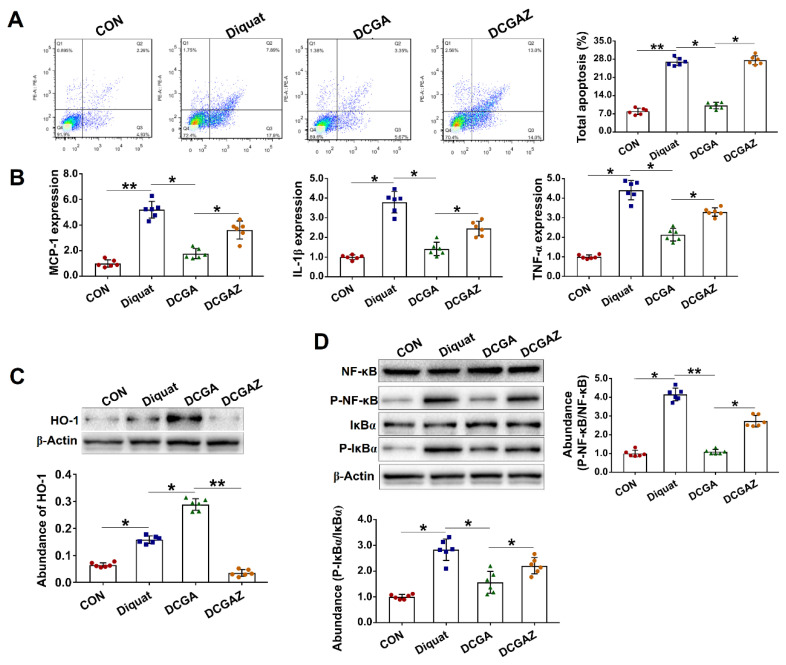
Figure 4.
Chlorogenic acid (CGA)-regulated heme oxygenase-1 (HO-1) expression suppresses NF-kappa-B inhibitor alpha (IκBα)/nuclear factor-κB (NF-κB) signaling in IEPC-J2 cell exposure to oxidative stress. (A) Analysis of cell apoptosis by flow cytometric assays. In each diagram, Q1 represents the percentage of nonviable and necrotic cells, Q2 represents the percentage of late apoptotic cells, Q3 represents the percentages of early apoptotic cells, and Q4 represents the percentage of live cells. IPEC-J2 cells were plated in 24-well plates at a density of 1 × 105 cells/well (n = 6). (B) qPCR analysis of the expression levels of critical inflammation-related molecules. (C) Western-blot analysis of the abundance of heme oxygenase-1 (HO-1). (D) Western-blot analysis of critical signaling proteins involved in the IκBα/NF-κB pathway. CON, cells without being treated; diquat, cells were treated by 100 µM diquat; DCGA, cells were pretreated by 100 µM CGA for 6 h and were then treated by 100 µM diquat for 3 h; DCGAZ, cells were pretreated by 10 µM Zn-protoporphyrin-IX (ZnPPIX, the specific inhibitor of HO-1) and were then treated by 100 µM CGA and 100 µM diquat. * p < 0.05, ** p < 0.01.