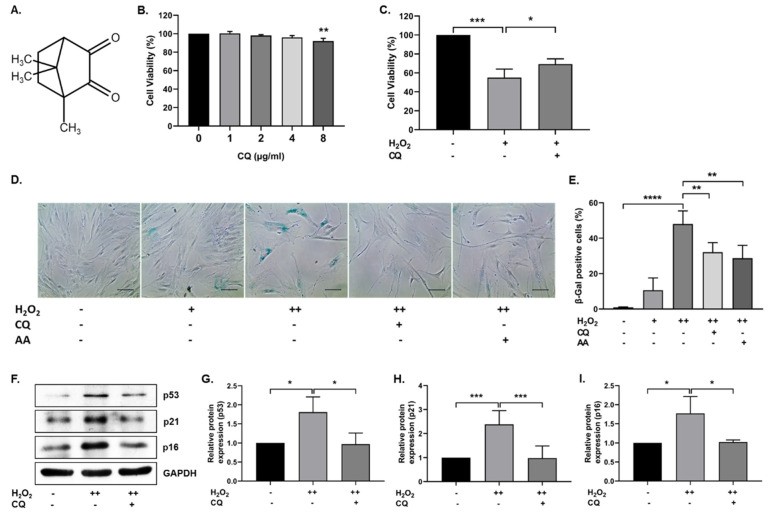
Figure 1.
Effect of Camphorquinone (CQ) on oxidative stress-induced senescence. (A) Chemical structure of camphorquinone (CQ). (B) Effect of CQ on cell viability was measured using the MTT assay (n = 3). (C) Protective effect of CQ (1 µg/mL) against H2O2 (0.7 mM) was confirmed via the MTT assay. (D) Representative image of SA-β-gal-positive cells in either single- or double-time H2O2 (200 µM) treatment and (E) percentage of SA-β-gal-positive cells in the oxidative-stress-induced senescence model (n = 4). (F) Representative images from the immunoblot assay against the senescence markers p53, p21, and p16; (G–I) the expression levels of target proteins were quantified using the ImageJ software. GAPDH was used as an internal control. H2O2 (+) represents a one-time treatment and H2O2 (++) represents double-time treatment. The scale bar represents 100 µm. All data are presented as mean ± standard deviation (SD) * p < 0.05, ** p < 0.01, *** p < 0.001 and **** p < 0.0001.