Fig. 1. LTC4 and IL-25 synergize for airway type 2 lung inflammation.
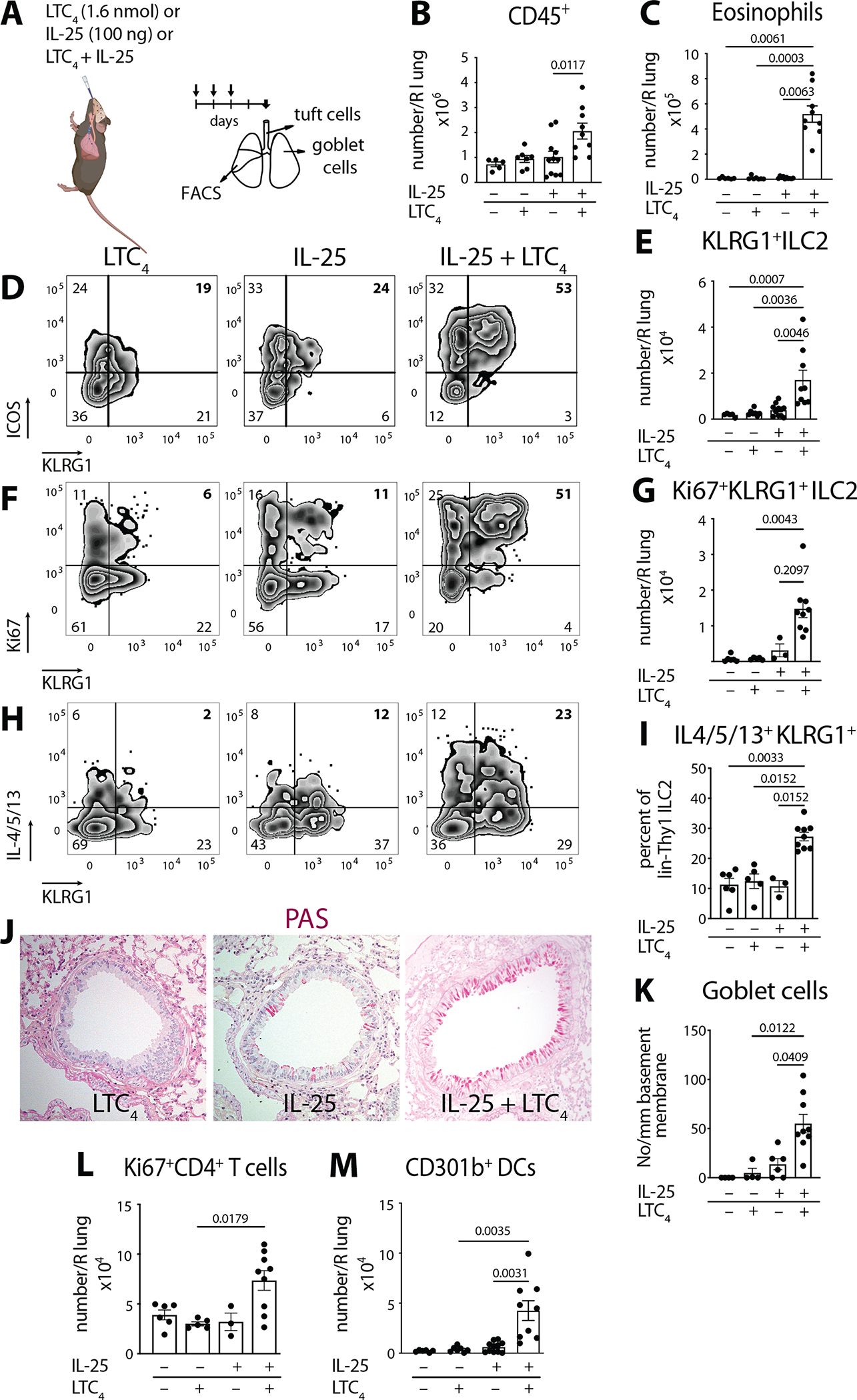
(A) WT mice (C57BL/6) were given three daily inhalations of LTC4 (1.6 nmol), or IL-25 (100 ng) or a combination of LTC4 and IL-25 and assessed 2 days after the last dose. (B) Number of CD45+ cells and (C) number of eosinophils in the right lung assessed by FACS. (D) lin−Thy1+ lung ILC2s were evaluated for expression of KLRG1 and ICOS. (E) Number of KLRG1+ ILC2s in the lung. (F) Intranuclear expression of Ki67 was assessed in lin−Thy1+ lung ILC2s together with KLRG1 surface staining. (G) Number of Ki67+ KLRG1+ ILC2s in the lung. (H) Lung ILC2 cytokine expression was assessed by intracellular staining for IL-4, IL-5 and IL-13 after Golgi plug treatment of lung single cell suspensions. (H) Percent of KLRG1+ IL-4/5/13 within the lin−Thy1+ lung ILC2s. (J) Goblet cell hyperplasia in cross sections of the lung assessed by Periodic acid Schiff (PAS) stain. (K) Goblet cells were enumerated per mm of basement membrane in the large bronchi. (L) Number of proliferating CD4+ T cells (Ki67+ CD4+ T cells) and (M) Number of CD301b+ DCs in the lung by FACS. Data are means ± SEM pooled from 3 independent experiments, each dot is a separate mouse, Kruskal-Wallis ANOVA with Dunn’s correction for multiple comparisons, p values <0.05 indicated.
