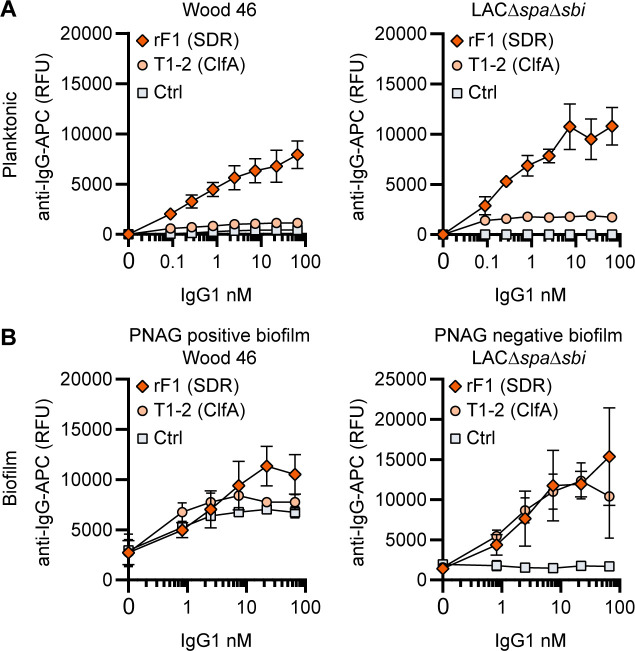
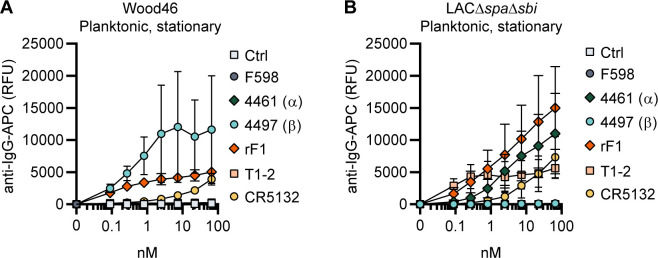
Figure 4. IgG1 monoclonal antibodies (mAbs) against protein components bind planktonic bacteria as well as biofilm.
(A) Planktonic bacteria of Wood46 (left) and LAC∆spa∆sbi (right) were grown to exponential phase and incubated with a concentration range of rF1-IgG1 or T1-2-IgG1. mAb binding was detected using APC-labeled anti-human IgG antibodies and flow cytometry and plotted as geoMFI of the bacterial population. (B) Biofilms of Wood46 (left) and LAC∆spa∆sbi (right) were grown for 24 hr and incubated with a concentration range of rF1-IgG1 or T1-2-IgG1. mAb binding was detected using APC-labeled anti-human IgG antibodies and a plate reader and plotted as fluorescence intensity per well. Data represent mean + SD of three independent experiments.