Figure 10.
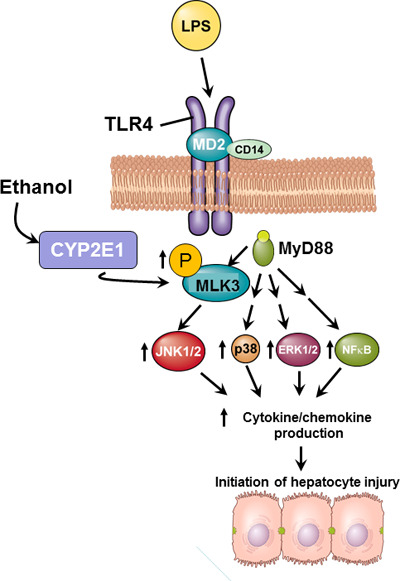
Schematic representation of the role of myeloid MLK3 in the progression of ethanol-induced liver injury. Ethanol feeding increases the phosphorylation of MLK3 in Kupffer cells; this increase is dependent on the activity of CYP2E1. Upon ligation of TLR4, MLK3 is an upstream activator of JNK and contributes, along with previously reported changes in p38, extracellular receptor kinase 1/2 (ERK1/2), and NF-κB signaling1,2, to the sensitization of TLR4-mediated cytokine and chemokine expression. Increased cytokine/chemokine expression contributes to ethanol-induced hepatocyte injury.
