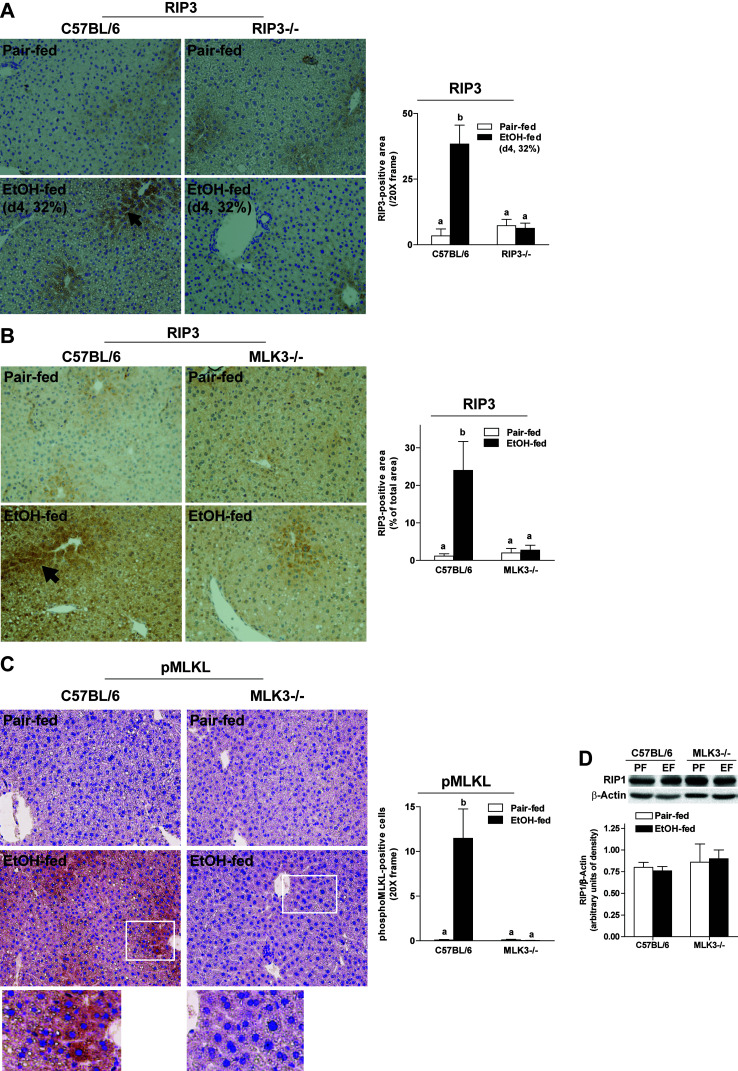
Figure 8.
Chronic ethanol feeding increased expression of RIP3 or phosphorylation of MLKL in both wild-type and MLK3−/− mice. (A) C57BL/6 and RIP3−/− mice were allowed free access to diets with increasing concentrations of ethanol (final concentration 32% of kcal) or pair fed a control diet for 4 days. (B–D) C57BL/6 and MLK3−/− mice were allowed free access to diets with increasing concentrations of ethanol (final concentration 32% of kcal) or pair fed a control diet for 25 days. Paraffin-embedded livers were deparaffinized followed by (A, B) RIP3 or (C) phospho-MLKL staining. Images were acquired using 20× objectives. The area positive for RIP3 or phospho-MLKL was quantified using Image-Pro Plus software and analyzed. (D) RIP1 protein was assessed via Western blot and quantified. Values represent means ± SEM, n = 4 pair-fed and 6 EtOH-fed mice. Values with different lower case letters are significantly different from each other, p < 0.05.