Figure 9.
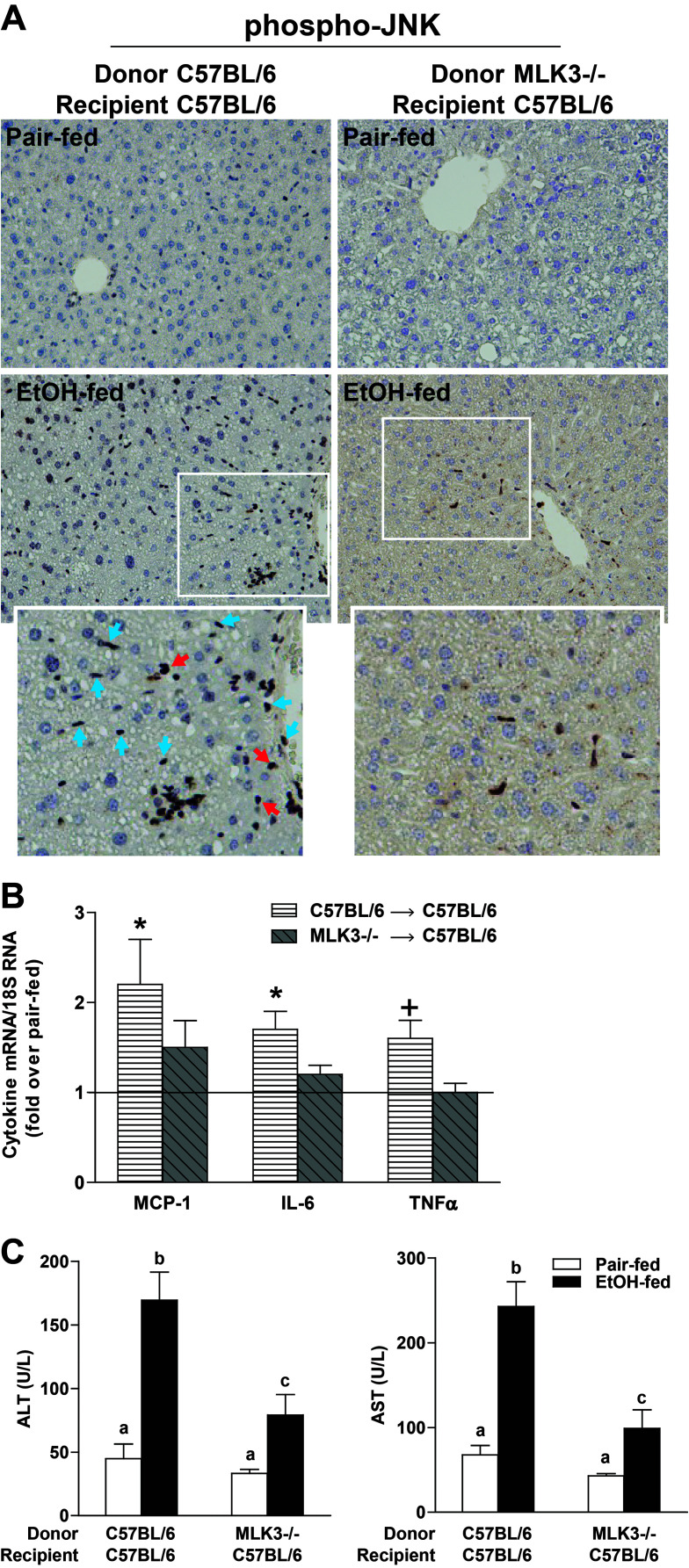
Myeloid MLK3 contributed to chronic ethanol-induced liver injury. C57BL/6 received wild-type bone marrow or MLK3−/− bone marrow. Chimeric mice were allowed free access to diets with increasing concentrations of ethanol (final concentration 32% of kcal) or pair fed a control diet for 25 days. (A) JNK phosphorylation was evaluated by immunohistochemistry in paraffin-embedded livers. Red arrows indicate hepatocytes, and blue arrows indicates nonparenchymal cells. (B) MCP-1, interleukin-6 (IL-6), and tumor necrosis factor-α (TNF-α) mRNA expression was detected in mouse livers using qRT-PCR measurement. *p < 0.05, +p < 0.07 compared to C57BL/6/C57BL/6 bone marrow-transplanted mice. (C) Enzyme activities of alanine aminotransferase (ALT) and aspartate aminotransferase (AST) were measured in plasma. Values with different lower case letters are significantly different from each other, p < 0.05. Values represent means ± SEM, n = 4 pair-fed and n = 6 EtOH-fed mice.