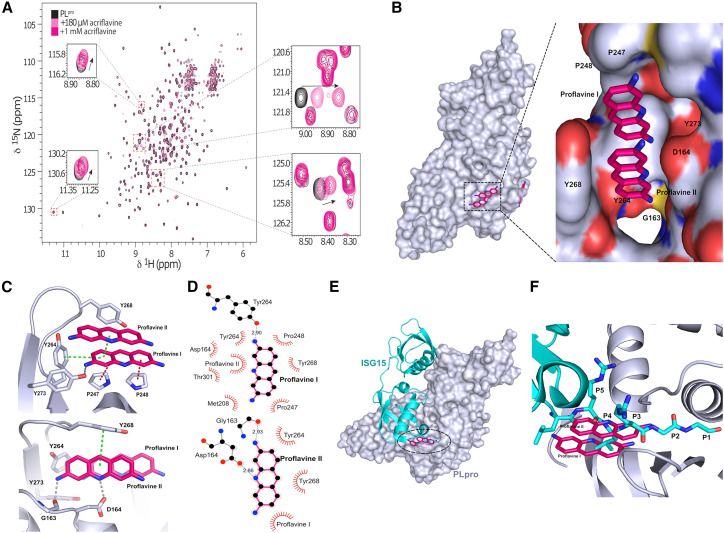
Figure 2.
Structural details of PLpro inhibition by proflavine
(A) 1H,15N heteronuclear correlation NMR spectra of 15N-labeled PLpro titrated with ACF indicate a localized binding.
(B) Crystal structure of PLpro-proflavine complex at 2.7 Å. The magnified fragment shows two proflavine molecules inside the substrate-recognition cleft of PLpro.
(C) Intermolecular interaction between PLpro and proflavine molecules. Two π-stacked molecules form a network of hydrogen bonds, π-π interactions, and hydrophobic contacts with PLpro.
(D) Molecular interaction details for the two proflavine molecules.
(E) Overlay of the ISG15-PLpro structure and PLpro-proflavine structure.
(F) A zoomed-in view of the binding pocket reveals that the proflavines are bound in the same site as the C-terminal end of the ISG15 substrate and mimic polar and lipophilic interactions of PLpro with the native substrate.