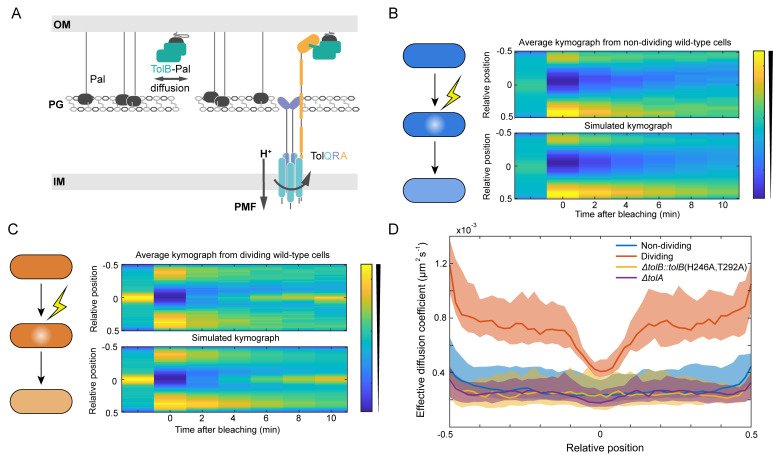
Fig 1. Pal in dividing cells is mobilised by TolQRA.
(A) Major components of the Tol-Pal system. Pal is an outer membrane (OM) lipoprotein (black) that can bind meso-diaminopimelic acid within peptidoglycan (PG) or the periplasmic protein TolB (green) in a mutually exclusive manner. The inner membrane (IM) protein TolA spans the periplasm and is coupled to the PMF via its interaction with TolQ and TolR. TolA is also able to interact with TolB and can form a tripartite complex of TolA-TolB-Pal [4]. (B) Top, average kymograph of Fluorescence Recovery After Photobleaching (FRAP) of Pal-mCherry over 30 non-dividing wild-type cells where the colour scale indicates normalised fluorescence. Bottom, simulated kymograph obtained using the SpatialFRAP method by fitting to the data above. (C) Same as in (B) for 30 dividing wild-type cells. (D) The effective diffusion coefficient of Pal as a function of the relative cellular location in individual non-dividing, dividing, ΔtolA, and ΔtolB::tolB(H246A, T292A) cells. TolB H246A T292A is a mutant that is unable to bind Pal. Shown is the median as a function of relative long axis position with 95% confidence intervals for approximately 30 cells. Data in (B)-(D) reproduced from reference [5].