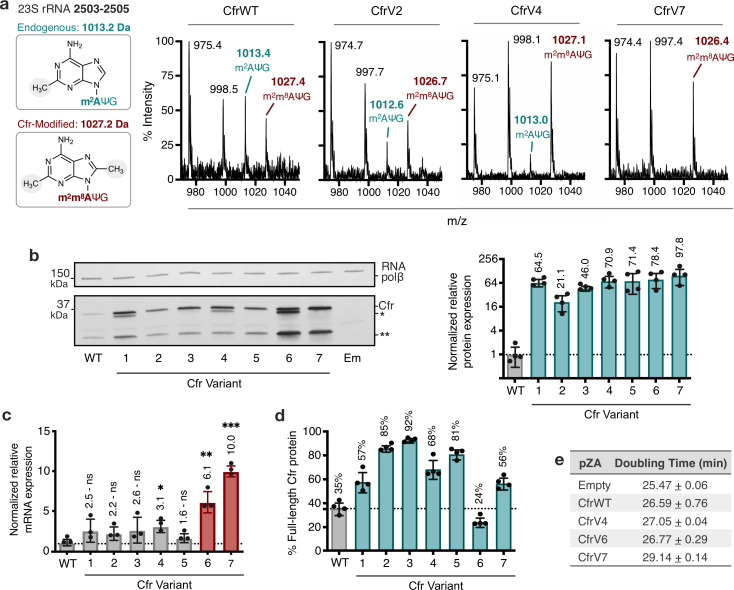
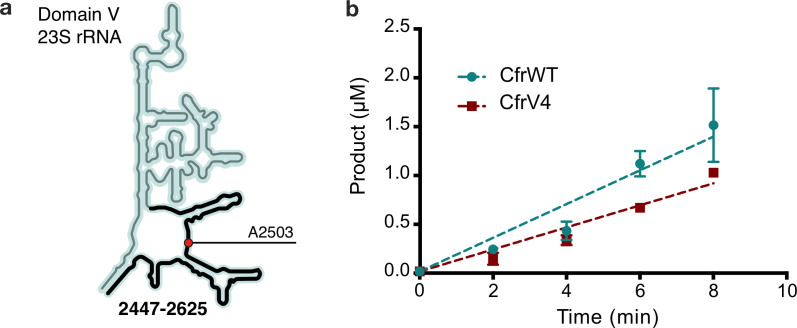
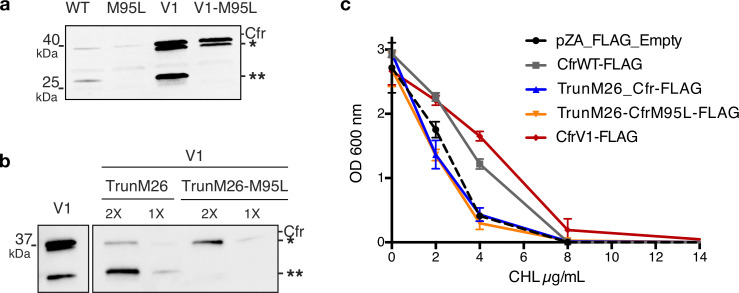
Figure 2. Cfr variants cause increased methylation of 23S rRNA at A2503, correlating with enhanced production of Cfr protein.
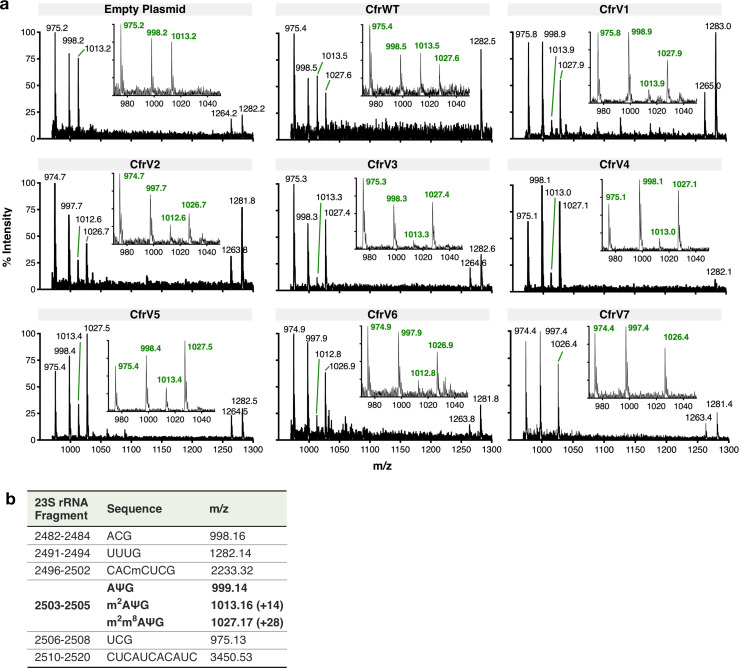
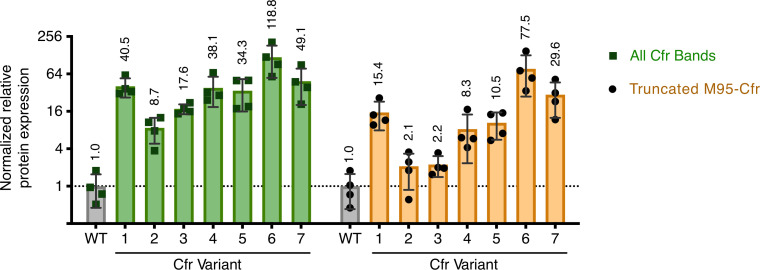
(a) Endogenously modified (m2A2503) and Cfr-hypermodified (m2m8A2503) rRNA fragments correspond to m/z values of 1013 and 1027, respectively. MALDI-TOF mass spectra of 23S rRNA fragments isolated from Escherichia coli expressing CfrWT, and evolved Cfr variants V2, V4, and V7. Ψ is pseudouridine, m2A is 2-methyladenosine, is m2m8A is 2,8-dimethyladenosine. (b) Relative protein expression of full-length Cfr variants compared to full-length CfrWT detected by immunoblotting against a C-terminal FLAG tag and quantification of top Cfr bands. Signal was normalized to housekeeping protein RNA polymerase β-subunit. Data are presented as the average of four biological replicates with standard deviation on a log2 axis. Asterisks denote N-terminally truncated versions of Cfr that do not contribute to resistance. Em = empty vector control. Original uncropped blot images are provided in Figure 2—source data 1. (c) Relative transcript levels for variants compared to CfrWT determined from three biological replicates with standard deviation. Statistical analysis was performed using a two-tailed t-test on log2 transformed data. (d) Percentage of total Cfr expression attributed to the production of full-length Cfr protein, presented as the average of four biological replicates with standard deviation. (e) Doubling times for E. coli expressing empty plasmid, CfrWT, or Cfr variants were determined from three biological replicates with standard error. Numerical data and exact p values where relevant for panels (b–d) are provided in Figure 2—source data 2.