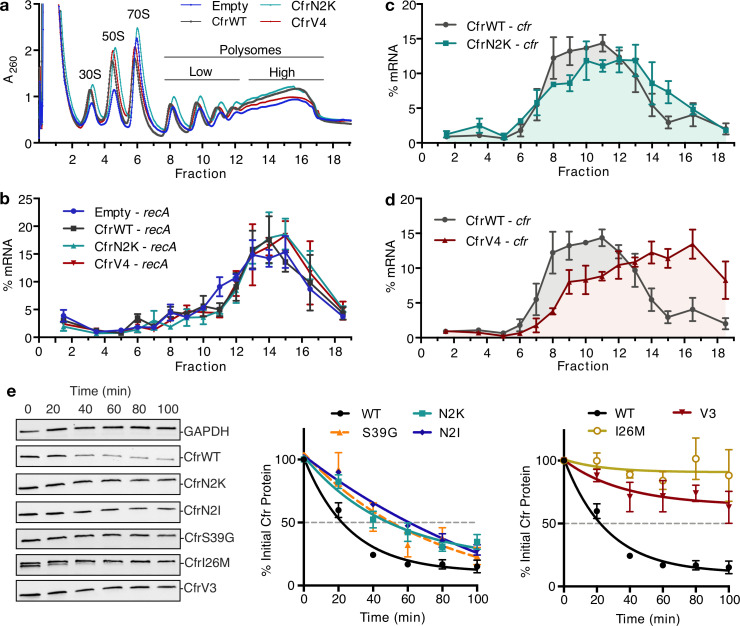
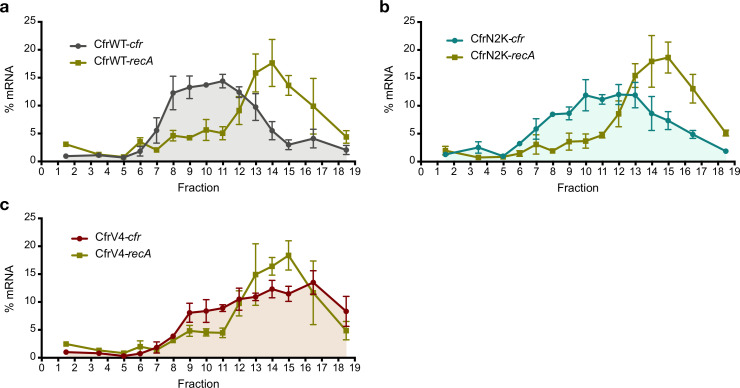
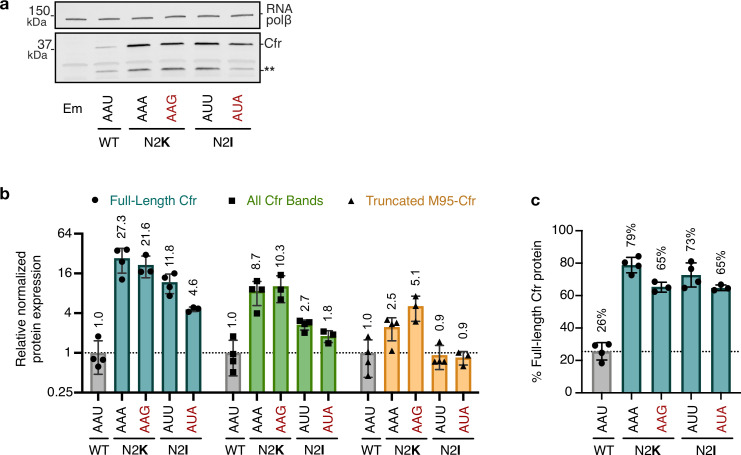
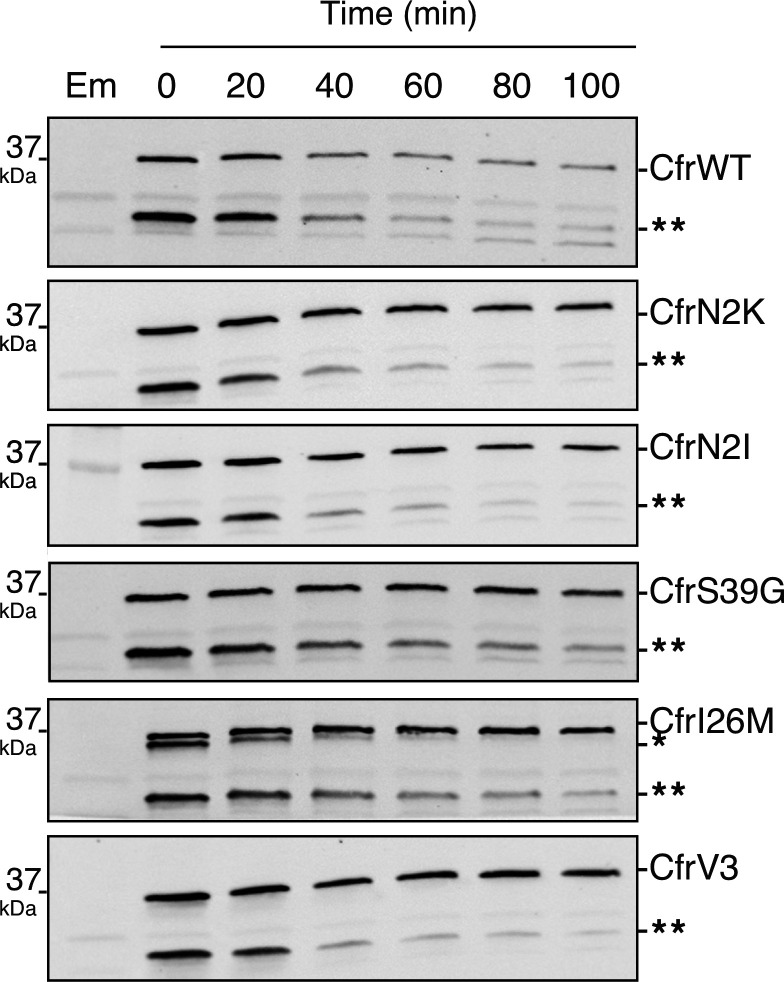
Figure 4. Directed evolution mutations impact Cfr translation and degradation.
(a) Sucrose gradient fractionation of polysomes from Escherichia coli expressing empty vector or CfrWT/N2K/V4 denoting fractions corresponding to low- and high-density polysomes. (b) mRNA distribution of well-translated, housekeeping gene recA across polysome profiles. (c) mRNA distribution of Cfr transcripts expressing CfrWT or CfrN2K. (d) mRNA distribution of Cfr transcripts expressing CfrWT or CfrV4. For (b–d), transcript levels for each fraction were determined by RT-qPCR and normalized by a luciferase mRNA control spike-in. Values presented as the average of three biological replicates with standard error. (e) Protein degradation kinetics of CfrWT, single mutations CfrN2K/N2I/S39G/I26M, and evolved variant CfrV3 in E. coli after halting expression by rifampicin treatment. Percentage of Cfr protein remaining over time was determined by immunoblotting against C-terminal FLAG tag and presented as the average of three biological replicates with standard error. Original uncropped blot images are shown in Figure 4—source data 1. Numerical data for all figure panels are provided in Figure 4—source data 2.