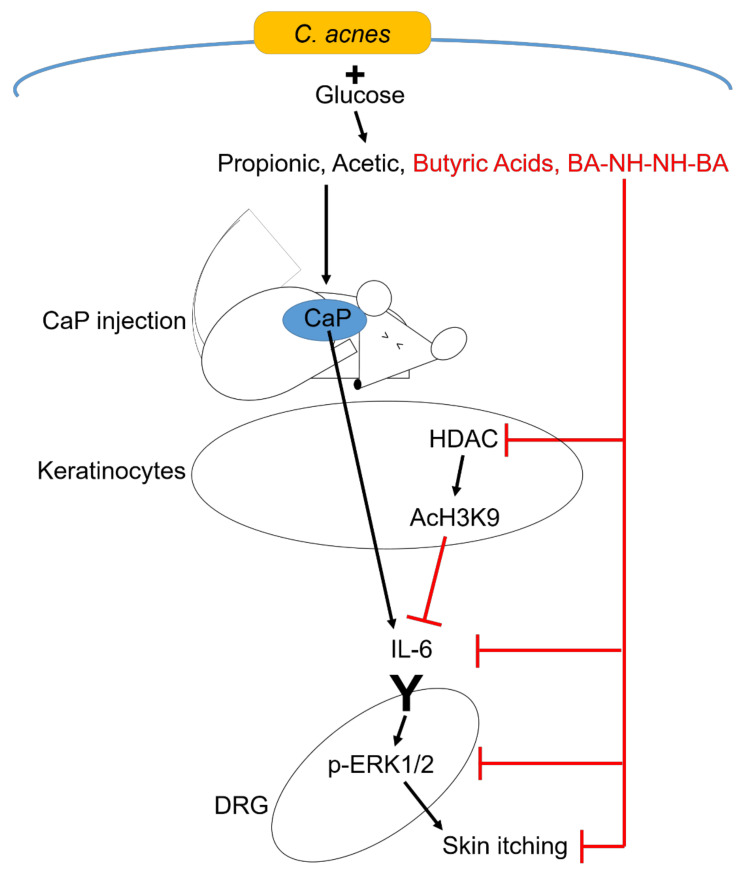
Figure 2. Antipruritic effect of butyric acid and mechanism of calcium phosphate in pruritus.
Image courtesy: Keshari S, Wang Y, Herr DR, et al. Skin cutibacterium acnes mediates fermentation to suppress the calcium phosphate-induced itching: a butyric acid derivative with potential for uremic pruritus. Journal of Clinical Medicine. 2020 Feb;9(2):312 [40]