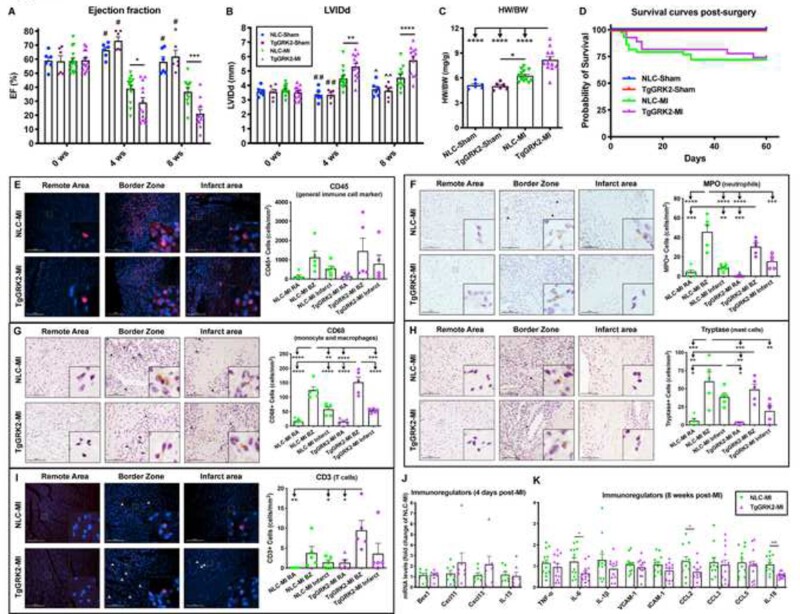
Figure 6.
Cardiomyocyte-specific GRK2 overexpression did not alter immune cell recruitment to the heart post-myocardial infarction. Ejection fraction (EF) (A) and left ventricular internal diameter in diastole (LVIDd) (B) as measured by echocardiography at 0 (baseline), 4- and 8-weeks post-Sham operation or myocardial infarction (MI) in NLC and TgGRK2 groups (n = 6–14). Measures of heart weight to body weight ratio (HW/BW) at 8 weeks post-surgery (C) (n = 6–13). Kaplan–Meier survival curves of Sham and MI groups (D) (n = 8–43). Log-rank (Mantel–Cox) test has been used between groups. Representative images and quantification of CD45 (E), MPO (F), CD68 (G), tryptase (H) and CD3 (I) stainings for remote area (RA), border zone (BZ), and infarct area of hearts from NLC and TgGRK2 mice at 4-days post-MI. Scale bar in white or black (100 μm). Arrowheads indicate positive staining. Insets show higher magnification at ×250 (n = 5 per group). Quantification of RT-PCR data showing fold change of NLC-MI for Bex1, Cxcl11, Cxcl13 and IL-15 (J) in LV samples collected at 4 days post-MI (n = 7 per group). Quantification of RT-PCR data showing fold change of NLC-MI for TNFα, IL-6, IL-1β, VCAM1, ICAM1, CCL2, CCL3, CCL5, and IL-18 (K) in LV samples collected at 8-weeks post-MI (n = 11–13). *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001, ****P < 0.0001, #P < 0.0001 vs. NLC-MI and TgGRK2-MI, ##P < 0.01 vs. NLC-MI and P < 0.0001 vs. TgGRK2-MI, ^P < 0.0001 vs. TgGRK2-MI, ^^P < 0.01 vs. NLC-MI P < 0.0001 vs. TgGRK2-MI. Two- or one-way ANOVA with Tukey’s post hoc test, t-test or Mann–Whitney test were used between groups.