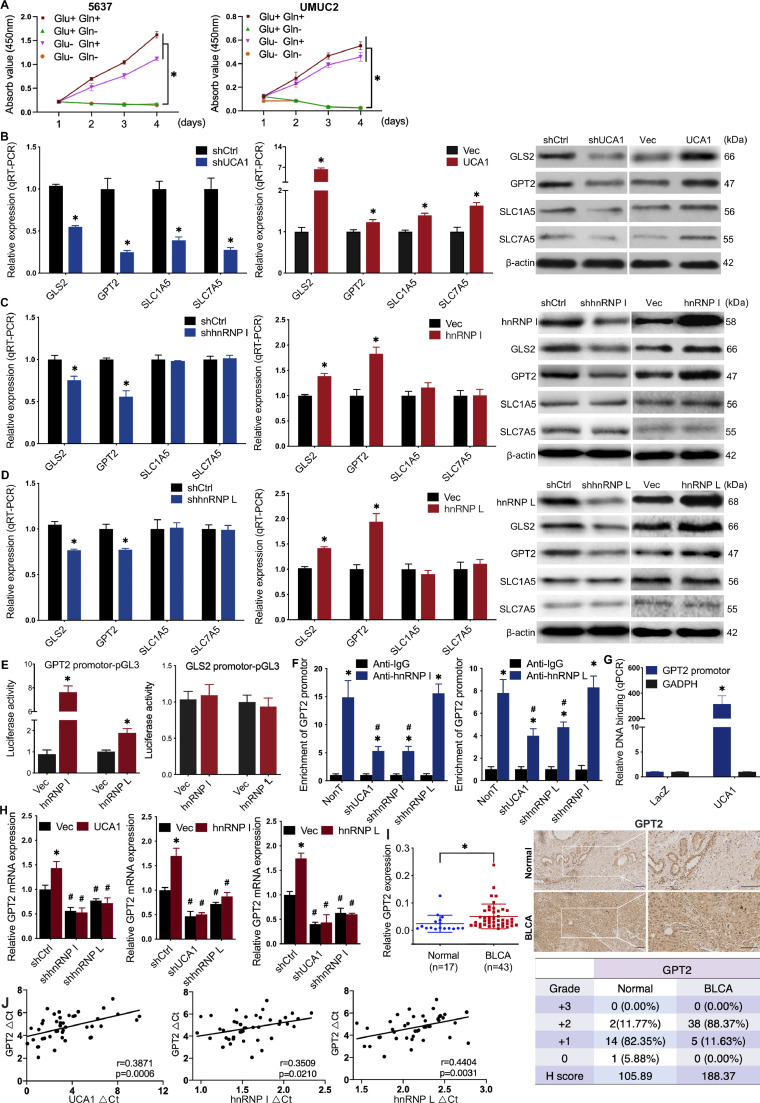
Fig. 4.
UCA1 regulates GPT2 expression by interacting with hnRNP I/L A, Glutamine more than glucose was required for the proliferation of BLCA cells. B to D, Screening of glutaminolysis associated enzymes: mRNA expression levels in UCA1 or hnRNP I/L knockdown and UCA1 or hnRNP I/L overexpressed BLCA cells were analyzed by qRT-PCR (left and middle). Protein levels were detected by western blot (right). E, Activation of the GPT2 promoter-pGL3 reporter by hnRNP I/L. Luciferase activity under the control of the GPT2 or GLS2 promoter was normalized to constitutively expressed renilla luciferase in 5637 cells transfected with control vector or hnRNP I/L plasmid. F, ChIP-qRCR detection of hnRNP I/L binding to the GPT2 promoter. Anti-IgG was used as the negative control. The fold enrichment of GPT2 promoter sequence in hnRNP I/L was normalized to IgG ChIP. *P < 0.01, compared with Anti-IgG; #P < 0.01 compared with NonT. G, CHIRP-qRCR detection of UCA1 binding to GPT2 promoter. UCA1 targeted probes and negative LacZ probes were used for ChIRP assay. The fold enrichment of GPT2 promoter or GADPH sequence in UCA1 CHIRP was normalized to LacZ CHIRP. H, Overexpression of UCA1 cannot rescue the reduction of GPT2 caused by hnRNP I/L knockdown. Overexpression of hnRNP I cannot rescue the reduction of GPT2 caused by hnRNP L knockdown either. I to L High expression of GPT2 in BLCA tissues: qRT-PCR of GPT2 (I) was performed using normal tumor-adjacent bladder tissues (n = 17) and BLCA tissues (n = 43), and Pearson's correlations of GPT2 (J) were calculated; IHC of GPT2 (K) was performed using clinical tissues, and H score (L) was determined. * P < 0.01. Scale bar = 200 μm.