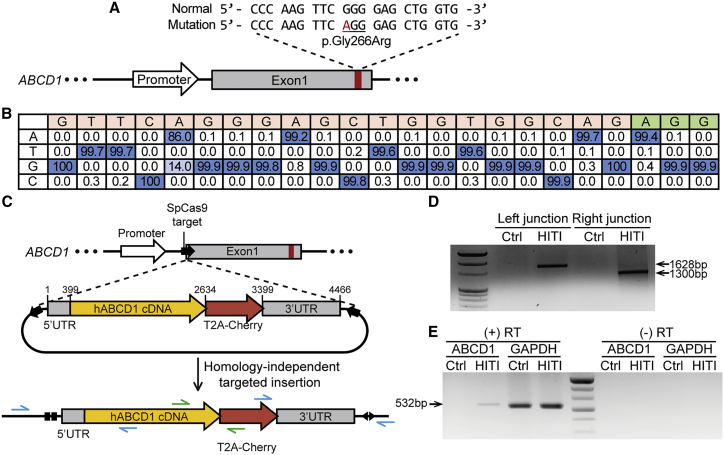
Figure 2.
Mutant ABCD1 gene rescue in patient-derived fibroblasts using ABE and HITI
(A) Schematic of WT and patient sequences. The disease-causing mutation is marked in red. (B) A sequence table showing the percentages of nucleotides at each position in the target sequence in patient-derived fibroblasts transfected with ABE. The PAM sequence is shown in green. (C) Scheme for integration of the normal hABCD1 cDNA near the endogenous 5′ UTR of ABCD1 by HITI. The blue arrows indicate the primers used to amplify the junctions between endogenous ABCD1 and the HITI donor after integration, and the green arrows indicate the primers used for RT-PCR. (D) Results from PCR analysis in which the integration junctions between endogenous ABCD1 and the HITI donor were amplified. (E) RT-PCR to confirm transcription from the HITI donor after integration. Expected band size of RT-PCR product for GAPDH is 536 bp. (+) RT, reverse transcriptase-positive sample; (−) RT, reverse transcriptase-negative sample.