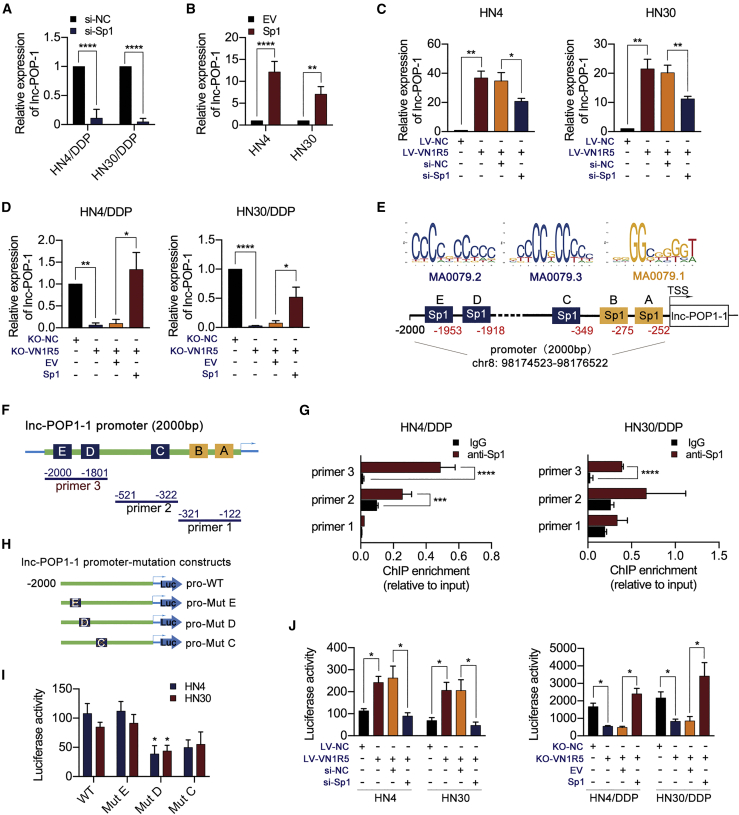
Figure 4.
VN1R5 regulated the promoter activity of Sp1 to affect lnc-POP1-1 expression
(A) lnc-POP1-1 expression was analyzed by qPCR in HN4/DDP and HN30/DDP cells with Sp1 knockdown. (B) lnc-POP1-1 expression was analyzed by qPCR in HN4 and HN30 cells overexpressing Sp1. (C) lnc-POP1-1 expression were analyzed by qPCR in VN1R5-overexpressing HN4 and HN30 cells with Sp1 knockdown. (D) lnc-POP1-1 expression were analyzed by qPCR in VN1R5-knockout HN4/DDP and HN30/DDP cells overexpressing Sp1. (E) The Sp1 binding motifs and predicted binding sites in the lnc-POP1-1 promoter were determined with AliBaba2.1 and JASPAR. (F) Primers specific for the promoter region including predicted TF binding sites were designed for ChIP assays. (G) ChIP-qPCR analysis of Sp1 genomic occupancy of the lnc-POP1-1 promoter in HN4/DDP and HN30/DDP cells. (H) Mutation constructs for Sp1 binding sites C, D, and E of the lnc-POP1-1 promoter were constructed. (I) The relative luciferase activity of mutation constructs for the lnc-POP1-1 promoter was measured. (J) The relative luciferase activity of the lnc-POP1-1 promoter was affected by VN1R5 and Sp1. ∗p < 0.05, ∗∗p < 0.01, ∗∗∗p < 0.001, ∗∗∗∗p < 0.0001. Error bars, means ± SDs. (ns, no significance; si, siRNA; EV, empty vector; TSS, transcription start site; WT, wild-type; Mut, mutation.)