Figure 3.
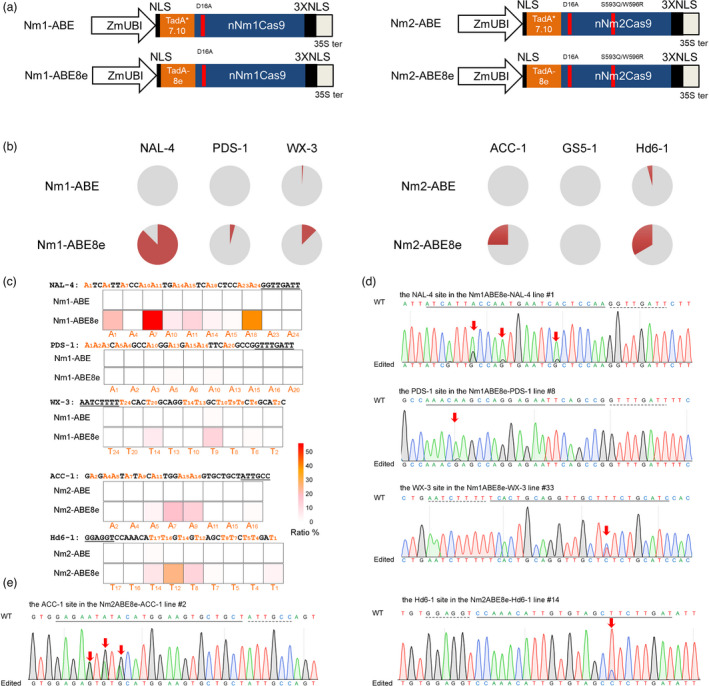
Nm‐ABEs introduce A‐to‐G conversions in rice. (a) Schematic representation of the ABEs derived from nNmCas9s. TadA*7.10 and TadA‐8e, evolved DNA adenine deaminases from E. coli TadA. (b) Frequency of mutants induced by Nm‐ABEs in the rice genome. For each sgRNA, 48–96 independent T0 lines were randomly selected and genotyped. Grey, wild type, no mutation was found at the target; red, plants harbouring base editing. (c) Heatmap of adenine base conversions induced by Nm‐ABEs. The target regions are indicated, and the positions of targetable nucleotides distal to the PAM are labelled. The substitution frequency of each base was calculated as the percentage of edited plants within the total plant population. (d) Sequencing chromatogram of edited plants. The A∙T‐to‐G∙C base conversion is labelled by a red arrow.
