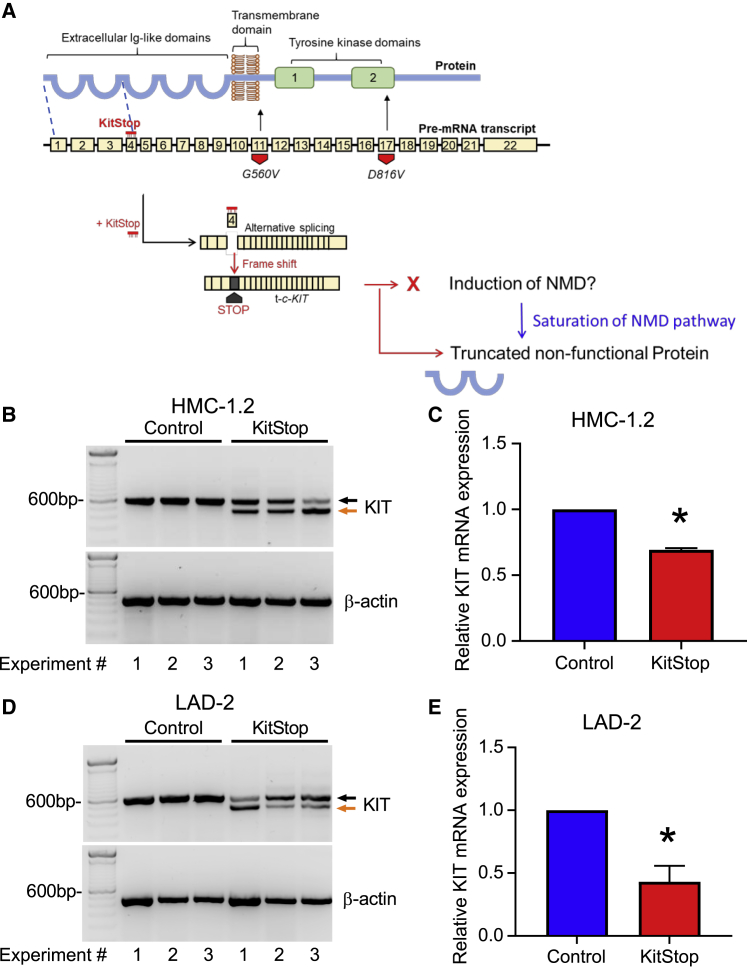
Figure 1.
ESO-mediated alternative splicing of exon 4 in c-KIT pre-mRNA
(A) KitStop ESO was designed to target the donor splice site of exon 4, which led to exclusion of exon 4 by the spliceosome. This is predicted to introduce a premature stop codon due to a frameshift in the open reading frame of the mRNA transcript, even in the presence of G560V and D816V activating mutations, which are located downstream of the target site of KitStop. The resulting premature stop codon was predicted to induce degradation of transcripts by NMD. If the NMD pathway becomes saturated, it was predicted that a truncated mRNA transcript encoding a non-functional protein would be produced. Yellow boxes represent exons; thick black bar represents introns. FL-c-KIT, full-length c-KIT; t-c-KIT, truncated c-KIT. (B) Gel electrophoresis data demonstrating splice switching of c-KIT by KitStop ESO in comparison to standard control (Stndcon) in HMC-1.2 as assessed by analysis of total RNA by RT-PCR. Black arrow indicates full-length c-KIT; orange arrow indicates alternatively spliced truncated c-KIT mRNA. Each lane of the gel represents a paired replicate for Stndcon- and KitStop-treated cells in sequence. Gel electrophoresis RT-PCR images were acquired using a LI-COR Odyssey Fc imaging system. (C) qRT-PCR of c-KIT transcripts in HMC-1.2 cells demonstrates a significant reduction in KIT mRNA transcripts with KitStop relative to Stndcon-treated cells after correction against the housekeeping gene β-actin. (D) Gel electrophoresis data demonstrating splice switching of wild-type c-KIT mRNA by KitStop ESO in comparison to Stndcon ASO in LAD2 cells. (E) qRT-PCR of c-KIT transcripts in LAD2 cells demonstrates a significant reduction with KitStop relative to Stndcon cells. Data include mean ± SEM from three independent experiments. ∗p < 0.05, one-sample t test against hypothetical mean of 1.