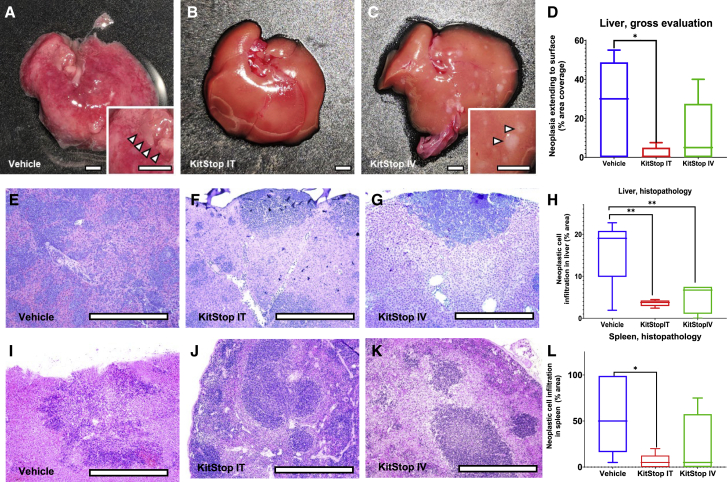
Figure 7.
KitStop ESO administration reduced multicentric spread to organs and tissues in an isograft model of mast cell neoplasia carrying D814Y auto-activating mutation of the c-Kit proto-oncogene
Multicentric neoplasia cells spread from the primary tumor site to infiltrate organs commonly involved in advanced cases of systemic mastocytosis, including liver, spleen, gastrointestinal tract, lymph nodes, and occasionally other tissues. (A–C) Representative images show grossly detectable neoplastic mast cell infiltration-replaced hepatic parenchyma (inset, arrowheads) as pale cream-colored irregular zones and nodules. (D) Percent of liver surface replaced by neoplastic mast cells was reduced for the i.t. (p = 0.0153) KitStop ESO treatment group compared to controls. (E–G) Histopathology sections of liver show infiltration by neoplastic cells in multifocal coalescing distribution in vehicle mice (E) and with KitStop treatment had multiple discrete foci (F and G). (H) Infiltration of neoplastic mast cells into liver was reduced for the i.t. (p = 0.0067) and i.v. (p = 0.0042) KitStop ESO treatment groups compared to controls. (I–K) Histopathology sections of spleen had infiltration by neoplastic cells as individualized cells and multifocal coalescing distribution infiltrating red (I–K) and white (I and K) pulp. (L) Infiltration of neoplastic mast cells into spleen was reduced for the i.t. (p = 0.0201) KitStop ESO treatment group compared to controls. (D, H, and L) Graphical representation of data includes boxplots where middle bar represents median and whiskers represent minimum and maximum. The p value was determined by a Fisher’s LSD test with an ordinary one-way ANOVA or uncorrected Dunn’s test with a Kruskal-Wallis one-way ANOVA. ∗p ≤ 0.05, ∗∗p ≤ 0.01. Scale bars, 0.5 cm.