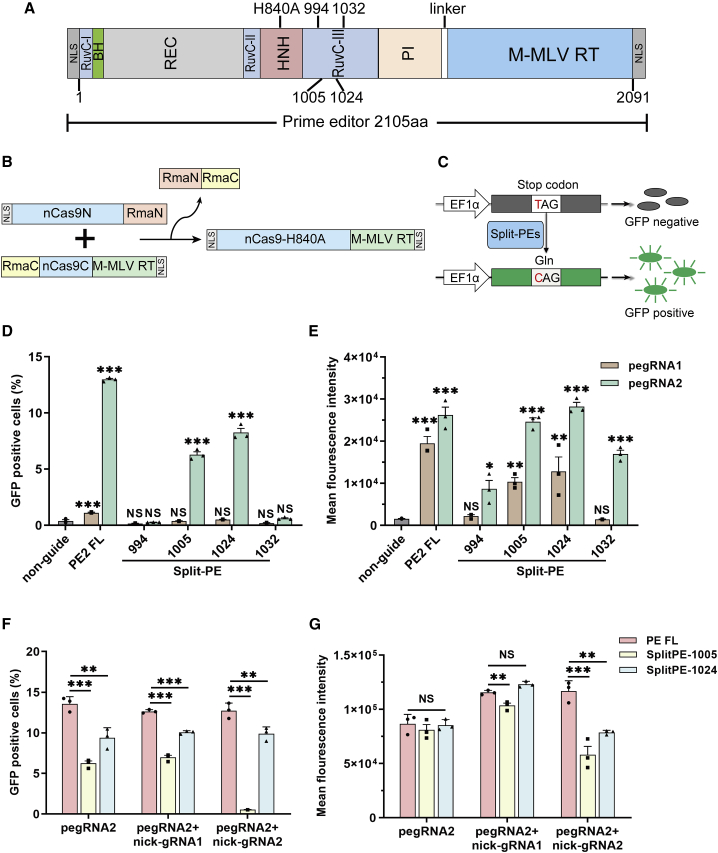
Figure 1.
Efficient T-to-C editing by Split-PEs in the reporter cells
(A) Schematic of split-PEs split at four different sites (994−995, 1,005−1,006, 1,024−1,025, and 1,032−1,033). RuvC, endonuclease domain; BH, bridge helix; REC, recognition domain; HNH, His-Asn-His endonuclease domain; PI, protospacer-adjacent motif (PAM)-interacting domain; M-MLV RT, engineered Moloney murine leukemia virus (M-MLV) reverse transcriptase (D200N, L603W, T306K, W313F, T330P). (B) Schematic of Rma intein-mediated PE reconstitution through protein trans-splicing. (C) Reporter cell harbors a mutated GFP (GFPm) coding sequencing, containing a premature stop codon in the GFP coding sequence, downstream of the EF1α promoter. The GFP signal would be detected by flow cytometer when the TAG codon was converted to the CAG codon by split-PE. (D) The percentage of GFP-positive cells after different split-PE and pegRNA treatment. (E) The mean fluorescence intensity after different split-PE and pegRNA treatment. (F) The percentage of GFP-positive cells after varying split-PE3 treatment in GFPm reporter cells. (G) The mean fluorescence intensity after different split-PE3 and pegRNA2 treatment. non-guide, reporter cells transfected with full-length PE2 but not pegRNA. PE2 FL, reporter cells transfected with full-length PE2 and pegRNA. Values and error bars represent the mean ± SD of three independent biological repeats. One-way ANOVA is used for calculating statistical significance (NS, not significant; ∗p < 0.05; ∗∗p < 0.01; ∗∗∗p < 0.001).