Figure 5.
Efficient editing of Dnmt1 in adult mouse eye by split-PE1024 delivered with dual AAVs
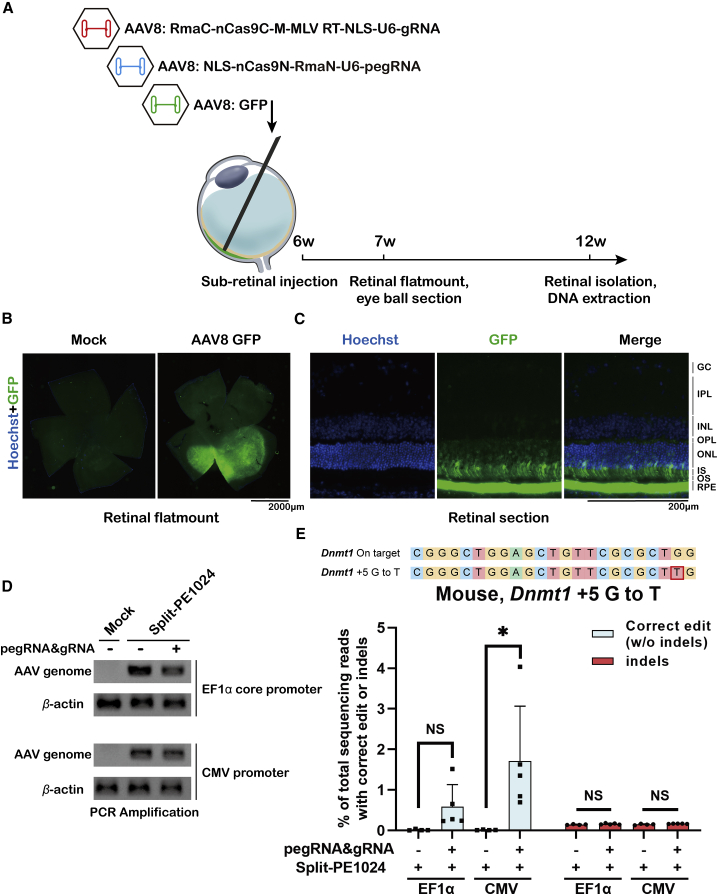
(A) Schematic illustration of subretinal injection. 1.1 × 1010 vg AAV8 (5 × 109 vg N-terminal half of split-PE1024 + 5 × 109 vg C-terminal half of split-PE1024 + 1 × 109 vg GFP) was injected into 6-week-old mouse retina. Mouse retina genomic DNA was isolated and extracted 6 weeks post-injection. (B) Representative retinal flat-mount showing variable GFP intensity and uneven distribution. 1 week post-injection of 109 vg AAV8-GFP, the mouse retina was isolated. Scale bar, 2,000 μm. (C) Fluorescence image of mouse retina section. RPE, retinal pigment epithelium; OS, outer segment; IS, inner segment; ONL, outer nuclear layer; OPL, outer plexiform layer; INL, inner nuclear layer; IPL, inner plexiform layer; GC, ganglion cell layer. Scale bar, 200 μm. (D) PCR amplification to detect the AAV genome in mouse retina injected with non-targeting or Dnmt1-targeting dual-AAV split-PEs with the EF1α or CMV promoter. Mock, noninjected control mouse retina. (E) Targeted editing efficiencies at the Dnmt1 site in adult mouse retina. Editing efficiencies represent sequencing reads that contain the correct edit and do not contain indels among total sequencing reads, which were analyzed by MATLAB and CRISPResso2. Indels were plotted for comparison. Retina injected with split-PE1024 and non-targeting pegRNA as the negative control. Values and error bars represent the mean ± SD of more than three independent mice eyes. t test was used for calculating statistical significance (∗p < 0.05).