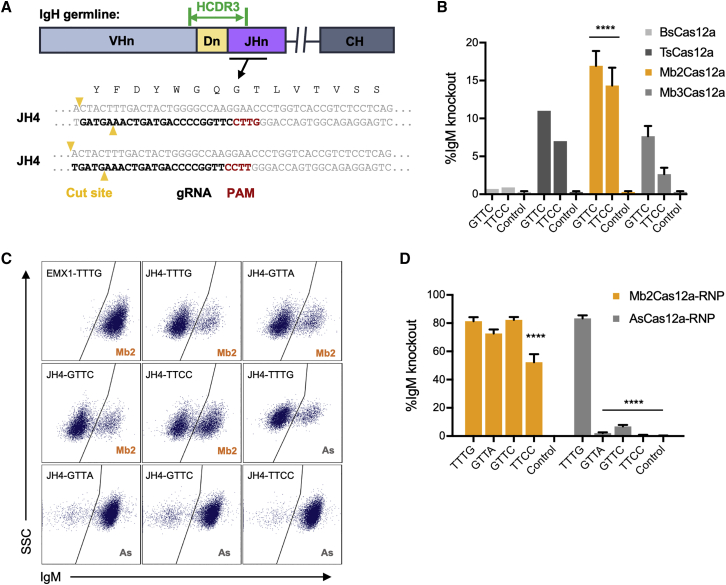
Figure 1.
Targeting the conserved region of JH4 gene requires a Cas12a ortholog recognizing non-canonical PAMs
(A) A representation of the coding region of an antibody heavy-chain variable region is presented. As indicated, the HCDR3 (green) is encoded by the 3′ of a recombined V gene, a D gene, and the 5′ of a J-chain. To insert a common HCDR3 into a diverse population of BCR, the gRNA of a CRISPR effector protein must complement a conserved HC region at the 3′ end of the recombined J-gene, while cleaving a more variable region near the site of HCDR3 insertion. Note that, unlike Cas9, Cas12a cleaves distally from its PAM and seed regions. The preferred PAM recognition sequence of commonly studied Cas12a orthologs is TTTV. However, as shown, JH4, the most frequently used JH gene in all species, contains optimally located GTTC and TTCC PAM sequences, located 3′ of the HCDR3-encoding sequence but oriented Cas12a cleavage within this sequence. This PAM, sequence of the gRNA, and the Cas12a cut sites are indicated. (B) To identify a Cas12a ortholog efficient at cleaving these non-canonical PAM motifs, the human B cell line Jeko-1 was co-transfected with two plasmids encoding the CRISPR protein (BsCas12a, TsCas12a, Mb2Cas12a, or Mb3Cas12a), and their corresponding gRNA. Control samples were transfected without gRNA plasmids. Targeting efficiency was measured by flow cytometry as loss of IgM expression. Among these Cas12a orthologs, Mb2Cas12 most efficiently cleaved the J-chain region initiated with GTTC and TTCC (orange). Error bars indicate standard error (SEM) of two independent experiments, and asterisks indicate statistical significance relative to controls. Statistical difference was determined by non-paired Student’s t-test (∗∗∗∗p < 0.0001). (C) Mb2Cas12a RNP was compared with commercial AsCas12a RNP for their ability cleave four distinct regions in the HCDR3-encoding region of Jeko-1 cells. Loss of IgM expression indicates successful introduction of a double-strand break and NHEJ. RNP with gRNA targeting an irrelevant site (EMX1) was used as control. (D) Results of three experiments similar to that shown in (B). Error bars indicate SEM of at least two independent experiments. Asterisks indicate significant differences from the canonical TTTG PAM (Mb2Cas12a or AsCas12a, respectively). Statistical difference was determined by non-paired Student’s t-test (∗∗∗∗p < 0.0001).