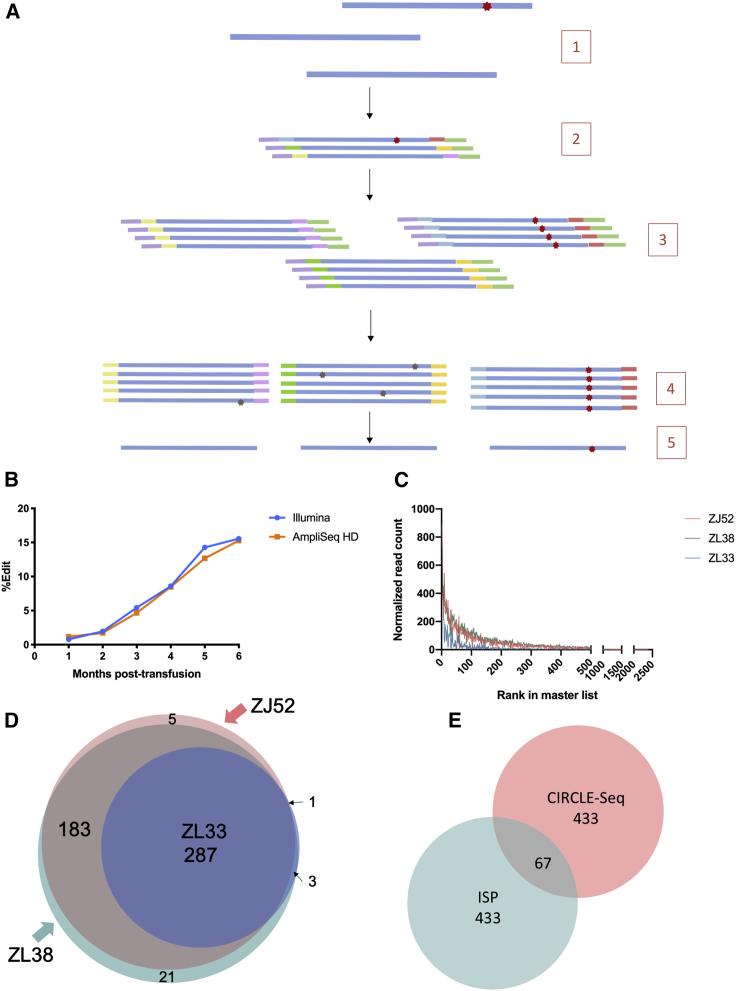
Figure 3.
AmpliSeq HD error-corrected sequencing panels
(A) AmpliSeq HD schematic. (1) Genomic DNA (blue) is extracted from cells, some with CRISPR mutations (red star). (2) The region of interest (on or off target) is amplified using the primer panel, adding UMIs to each end (different colors) and 5′ and 3′ universal adaptors (purple and green, respectively). (3) Each UMI-labeled molecule is amplified redundantly. (4) The molecules are sequenced and computationally sorted into molecular families based on the UMI. (5) A consensus sequence for each molecular family is computed. (B) Quantitation of on-target editing in TET2-edited RM ZL26 with Illumina targeted sequencing versus AmpliSeq HD is shown. (C) Read counts of each CD33 CIRCLE-seq site for the three animals individually are shown. (D) The source and overlap of the 500 CIRCLE-seq sites selected for AmpliSeq HD are shown. (E) Source (ISP and/or CIRCLE-seq) for the 1,000 sites selected for AmpliSeq HD is shown.