Figure 1. High-throughput in vivo screening and quartz crystal microbalance with dissipation monitoring (QCM-D) to quantify LNP delivery and protein adsorption properties.
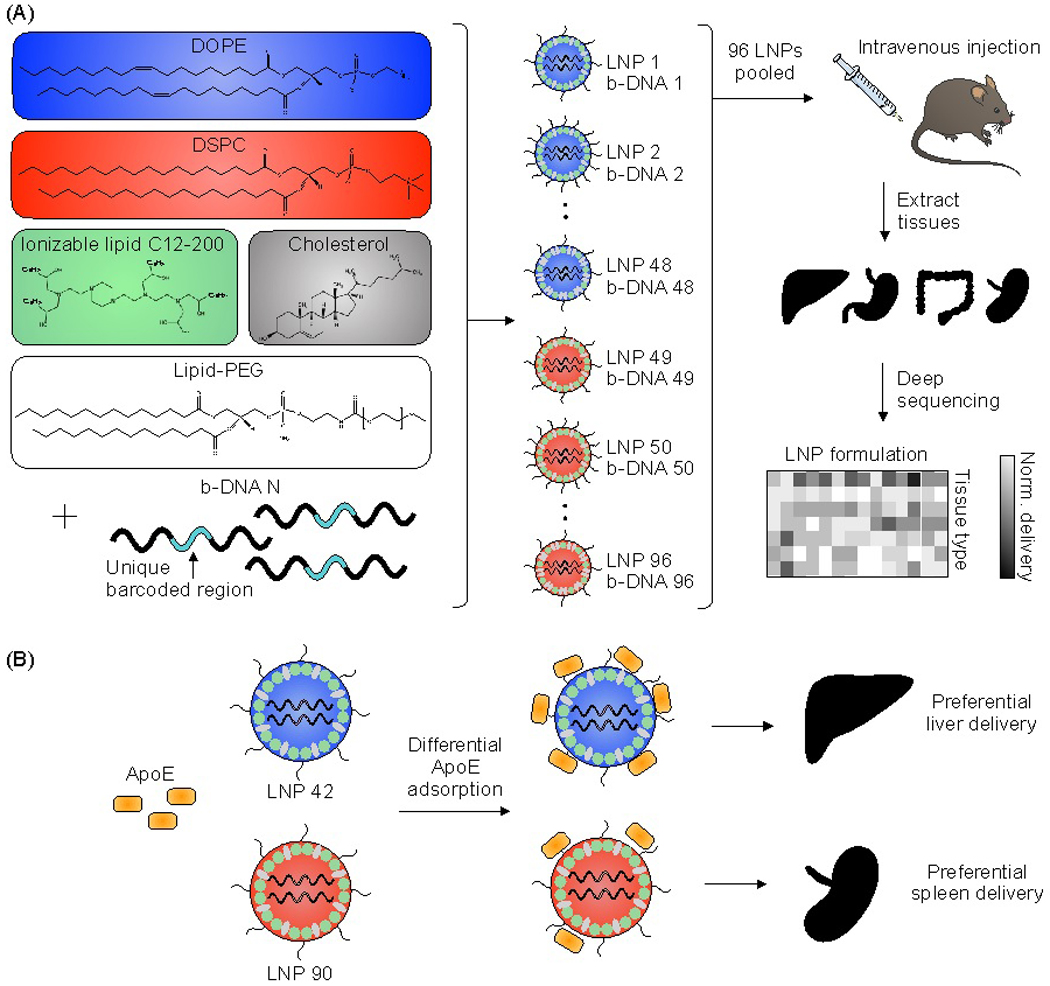
(A) LNPs were formulated with 1 ionizable lipid (C12–200), 6 different excipient molar ratios, 2 different ionizable lipid:b-DNA weight ratios, 2 different helper lipids, and 4 different lipid-anchored polyethylene glycol (PEG) conjugates (lipid-PEG) for a total of 96 LNP formulations. Details regarding the specific excipient molar ratios for each LNP are provided in Table S1. LNPs were formulated by pipette mixing to encapsulate barcoded DNA (b-DNA). LNPs were pooled together and injected to C57BL/6 mice via tail vein (N=4). Tissues were isolated six hours post-injection and accumulation of b-DNAs was quantified by deep sequencing. (B) Differences in LNP accumulation in the liver and spleen were identified and QCM-D was used as a means of measuring the interactions between LNPs and apolipoprotein E (ApoE).
