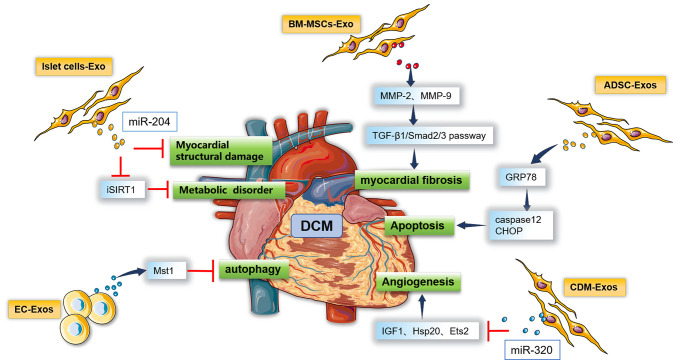
Figure 3.
Role of exosomes in the pathogenesis of DCM. BM-MSCs-Exo carry molecular targeting proteases, such as plasmin, MMP-2 and MMP-9, which activate the TGF-β1/Smad2/3 signaling pathway, thereby promoting cardiac muscle fibrosis. miR-204 carried by islet cells-Exo inhibits the expression of iSIRT1, aggravating myocardial energy mechanism disorders. ADSC-Exos activate the key promoters of the cardiomyocyte apoptosis pathway, caspase12 and CHOP, by targeting GRP78, inducing cardiomyocyte apoptosis. miR-320 carried by CDM-Exos inhibits IGF1, Hsp20 and Ets2, inhibiting cardiac endothelial cell migration and blood vessel formation. EC-Exos release Mst1, inducing cardiomyocyte apoptosis. DCM, diabetic cardiomyopathy; BM-MSCs-Exo, exosomes derived from bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells; ADSC, adipose-derived stem cells; iSIRT1, insulin receptor substrate 1; miR, microRNA; IGF, insulin-like growth factor; Hsp, heat shock protein; CHOP, C/EBP-homologous protein; CRP78, 78-kD glucose-regulated protein; CDM, cardiomyocyte; Ets2, E26 transformation-specific proto-oncogene 2; Mst1, mammalian ste20-like kinase-1; EC, endothelial cell.