Table 1.
Summary of Chemical Structures, Molecular Weight (MW), Values of Consensus Log Po/w, TPSA, Log S, Log BB, Log PS, H-Bond Donor, H-Bond Acceptor and Free Rotatable Bonds of the Tested mGlu5 NAMs
| Name | Structure | M.W.a | Cons. LogPo/wa | TPSAa | LogSa (Log mol/L) | LogBBb | LogPSb | H-bond donorc | H-bond acceptorc | Free rotatable bondc |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| MPEP |
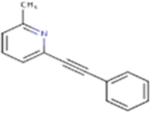
|
193.24 | 3.15 | 12.89 Å2 | −3.008 | 0.449 | −1.415 | 0 | 1 | 0 |
| Fenobam |
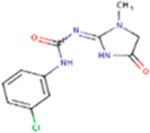
|
266.68 | 1.25 | 73.80 Å2 | −2.753 | −0.587 | −2.433 | 2 | 6 | 4 |
| FQ056 |
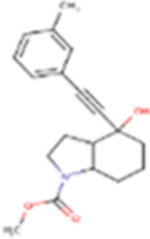
|
313.39 | 2.85 | 49.77 Å2 | −3.731 | 0.711 | −1.894 | 1 | 3 | 3 |
| G7090 |
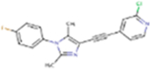
|
325.77 | 4.16 | 30.71 Å2 | −3.035 | 0.04 | −1.48 | 0 | 3 | 3 |
| ZD2066 |
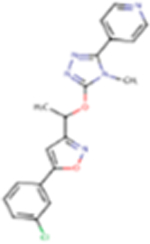
|
381.82 | 3.28 | 78.86 Å2 | −2.89 | −1.189 | −2.961 | 1 | 6 | 5 |
Predicted values from SwissADME (http://www.swissadme.ch30) including log Po/w (partition coefficient between n-octanol and water), an indicator of lipophilicity. The consensus (cons.) log Po/w is the average value of the five available predictive models in SwissADME. The topological polar surface area (TPSA), defined as the surface sum over all polar atoms or molecules, is a measure of permeability in that molecules > 140 Å2 are unlikely to permeate the blood brain barrier.
Predicted values from http://biosig.unimelb.edu.au/pkcsm/prediction.38 The water solubility of a compound (log S) reflects the solubility of the molecule in water at 25 °C. For a given compound, a log BB > 0.3 can readily cross the blood-brain barrier (BB), while molecules with log BB < −1 are poorly distributed in the brain. Compounds with a log PS > −2 are predicted to penetrate the CNS, while those with log PS < −3 are unlikely to cross the BBB or CNS membranes.39
The numbers of H-bond donor, H-bond acceptor, and free rotatable bonds of each NAM were obtained from PubChem (https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/) and The IUPHAR/BPS Guide to PHARMACOLOGY (https://www.guidetopharmacology.org/).
