FIGURE 1. miRNAs control the differentiation and function of distinct T cell subsets.
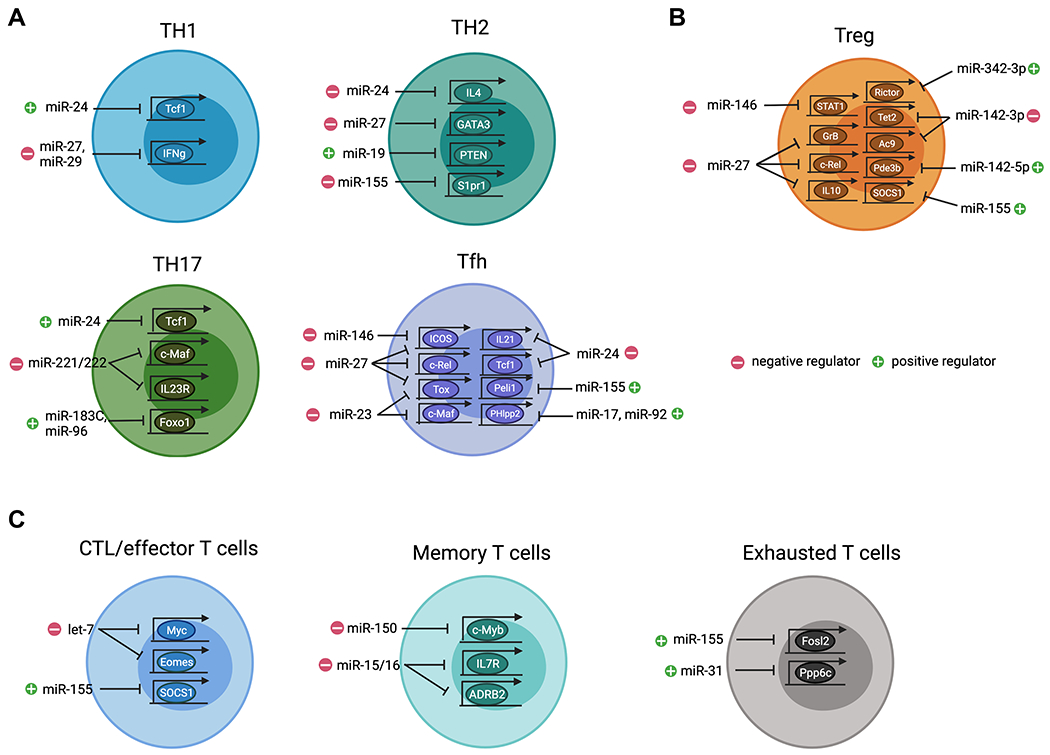
(A) Different miRNAs function either as positive or negative regulators in regulating CD4 Th cell responses. In Th1 cells, miR-24 promotes IFNγ responses through targeting Tcf7 whereas miR-27 and miR-29 inhibit IFNγ expression. In Th2 cells, miR-24, miR-27 and miR-155 serve as negative regulators by targeting, Il4, Gata3, and S1pr1, respectively, whereas miR-19 promotes Th2 cell response through targeting Pten. In Th17 cells, miR-24 and miR-183C promotes their function by inhibiting targeting Tcf7 and Foxo1, respectively, whereas miR-221/miR-222 negatively regulating Th17 cells by targeting Maf and Il23r. In Tfh cells, miR-23C (including miR-23, miR-24, and miR-27) and miR-146a/b coordinately restrict their responses by targeting, Maf, Tox, Il21, Tcf7, Rel, and Icos, respectively whereas miR-155 and miR-17/92 promote Tfh cells by targeting Peli1 and Phlpp2. (B) Development, maintenance, homeostasis, and function of Treg cells are regulated by different miRNAs. Specifically, miR-27, miR-142-3p, and miR-146a act as negative regulators in Treg cells by targeting Rel, Gzmb, Il10, Tet2, Ac9, and Stat1, respectively, whereas miR142-5p, miR-155, and miR-342-3p are essential to promote Treg cell homeostasis and function by targeting Pde3b, Socs1, and Rictor, respectively. (C) Distinct miRNAs regulate CD8 T cell immunity. In particular, let-7 and miR-155 serving as negative and positive regulators to control effector function by targeting Myc, Eomes and Socs1, respectively. Moreover, miR-150-mediated control of Myb and miR-15/16-mediated control of Il7r and Adrb2 respectively impacts memory T cell formation. Finally, both miR-31 and miR-155 promote T cell exhaustion by targeting Fosl2 and Ppp6c, respectively. All graphics are created with BioRender.com.
