FIGURE 2. T cell-extrinsic roles of miRNAs in regulating T cell immunity.
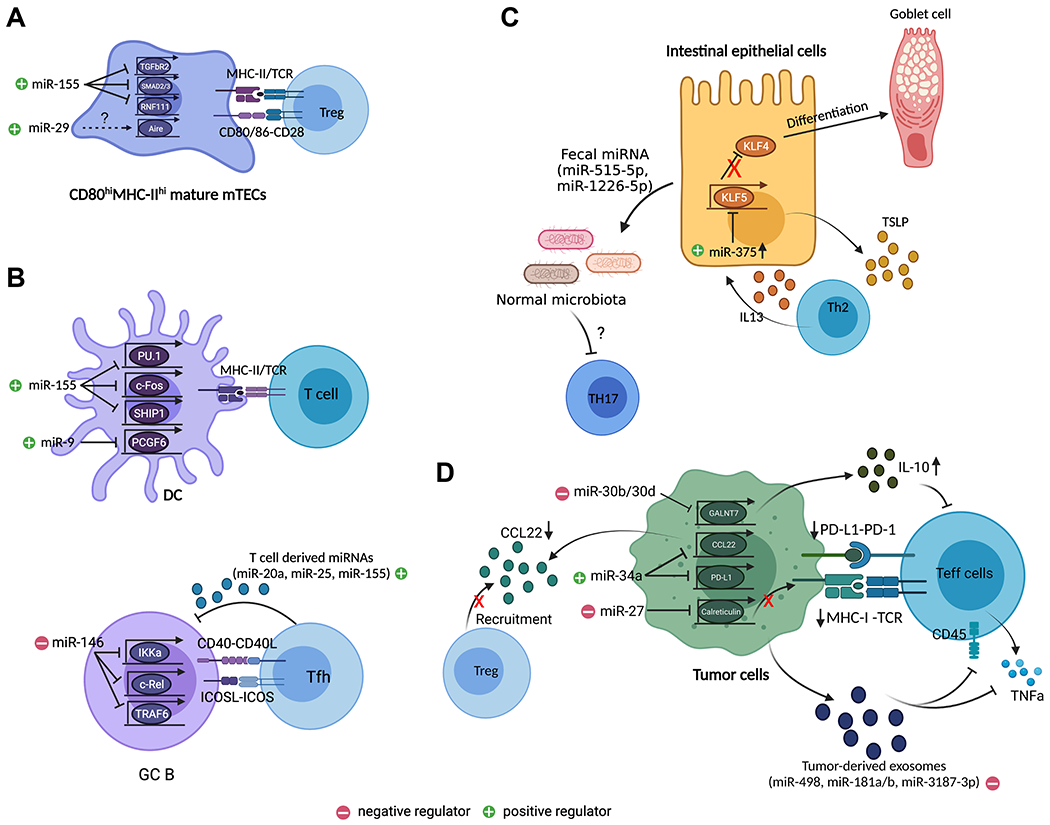
(A) miR-29 is required for the development of Aire+ mTEC while miR-155 safeguards mTEC maturation that is required for optimal thymic Treg cell development by targeting many components within the TGFβ signaling pathway including Tgfbr2, Smad2/3, and Rnf111. (B) In the periphery, miRNAs impact T cell responses through regulating their interacting partners. In DCs, miR-155 promotes their maturation and function through targeting Spi1 (encodes for PU.1), Fos, and Ship1. Similarly, miR-9 enhances function of DCs, cDC1s in particular, through targeting Pcgf6. In B cells, miR-146a limits GC B cell differentiation by targeting many signaling components downstream of CD40 signaling pathway including Ikka, Rel, and Traf6, which in turn impacts Tfh cell responses. On the other hand, exosomal miRNAs such as miR-20a, miR-25, and miR155, released from Tfh cells can promote GC B cell responses. (C) miRNAs can also affect T cell responses through shaping the tissue microenvironment. For example, in the intestine, miR-375 promotes IEC differentiation and function by targeting Klf5. Loss of miR-375 resulted in impaired TSLP secretion leading to defective intestinal Th2 immunity. Moreover, IEC-derived miRNAs, miR-515-5p and miR-1226-5p can regulate Th17 responses in the gut through targeting gut microbiota. (D) In tumor, downregulation of tumor suppressor miRNA, miR-34a led to enhanced Treg cell recruitment and impaired Teff cell activation due to the loss of miR-34a-mediated inhibition of CCL22 and PD-L1. On the other hand, miR-27 and miR-30b/d serve as oncomiRs by impairing MHCI-mediated antigen presentation and by promoting the production of immunosuppressive cytokine, IL-10 through targeting Calreticulin and Galnt7, respectively. Finally, tumor cell-derived exosomal miRNAs such as miR-181a/b, miR-498, miR3187-3p can also directly inhibit Teff cell function by targeting Cd45 and Tnf. All graphics are created with BioRender.com.
