Figure 4.
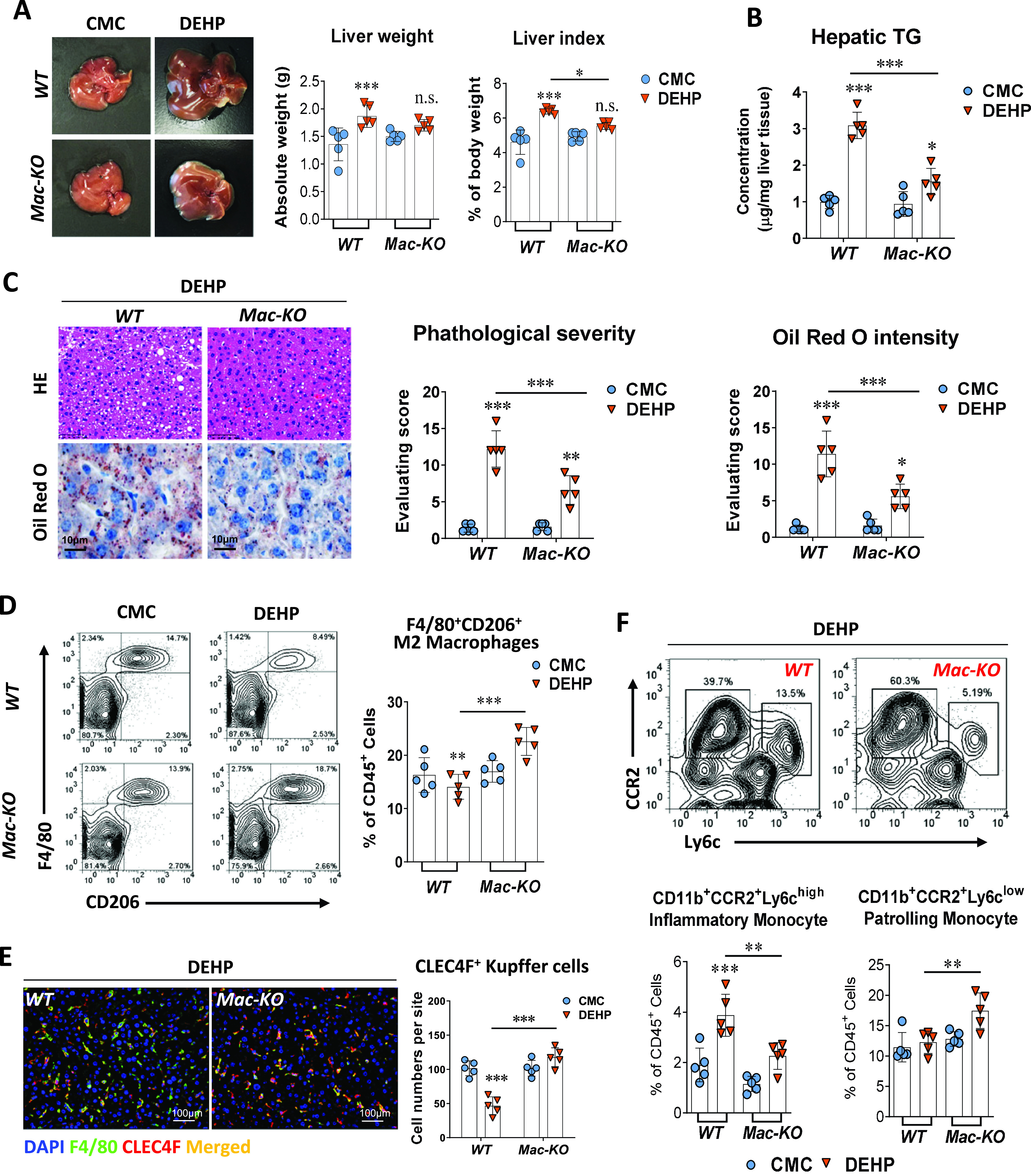
Effect of macrophage-specific knockout in DEHP-induced fatty liver. Wild-type (WT, ) and macrophage-specific knockout (Mac-KO, ) C57BL/6J male mice were treated with 0.5% (wt/vol) sodium carboxymethylcellulose (CMC; vehicle control) or DEHP ( BW) by daily gavage for 28 d. (A) Representative image of mice livers and quantification of liver weight and liver index at the end of the treatment (). The data are provided in Table S19. (B) Hepatic TG concentration in the liver tissue of WT () and Mac-KO () mice at the end of the treatment. The data are provided in Table S20. (C) Representative images of histology and Oil Red O staining of mouse liver at the end of the treatment (left). Hepatic steatosis and lipid accumulation were quantified by calculating the score of pathological severity and Oil Red O staining intensity, respectively (right, ). The data are provided in Table S21. (D) Representative flow cytometry gating graph and quantification of hepatic M2 macrophages () in the WT or Mac-KO () mice at the end of the treatment. The data are provided in Table S22. (E) Immunofluorescence staining of CLEC4F (red) and F4/80 (green) in the mouse liver of WT or Mac-KO mice () at the end of the treatment. Cells with positive stain of CLEC4F in the liver sections of WT and Mac-KO mice () were quantified using the ImageXpress system under . The data are provided in Table S23. (F) Representative flow cytometry gating graph and quantification of inflammatory monocyte () and patrolling monocyte () in the liver of WT or Mac-KO mice () at the end of the treatment. The data are provided in Table S24. All data are expressed as . The data were analyzed using two-way ANOVA followed by Tukey’s multiple comparisons test. *, **, *** compared with the vehicle control (i.e., CMC); significance of comparison between WT and Mac-KO groups of DEHP treatment was labeled above lines. Note: ANOVA, analysis of variance; BW, body weight; DAPI, 4′,6-diamidino-2-phenylindole; DEHP, diethylhexyl phthalate; HE, hematoxylin and eosin; SD, standard deviation; TG, triglyceride.
