Figure 6.
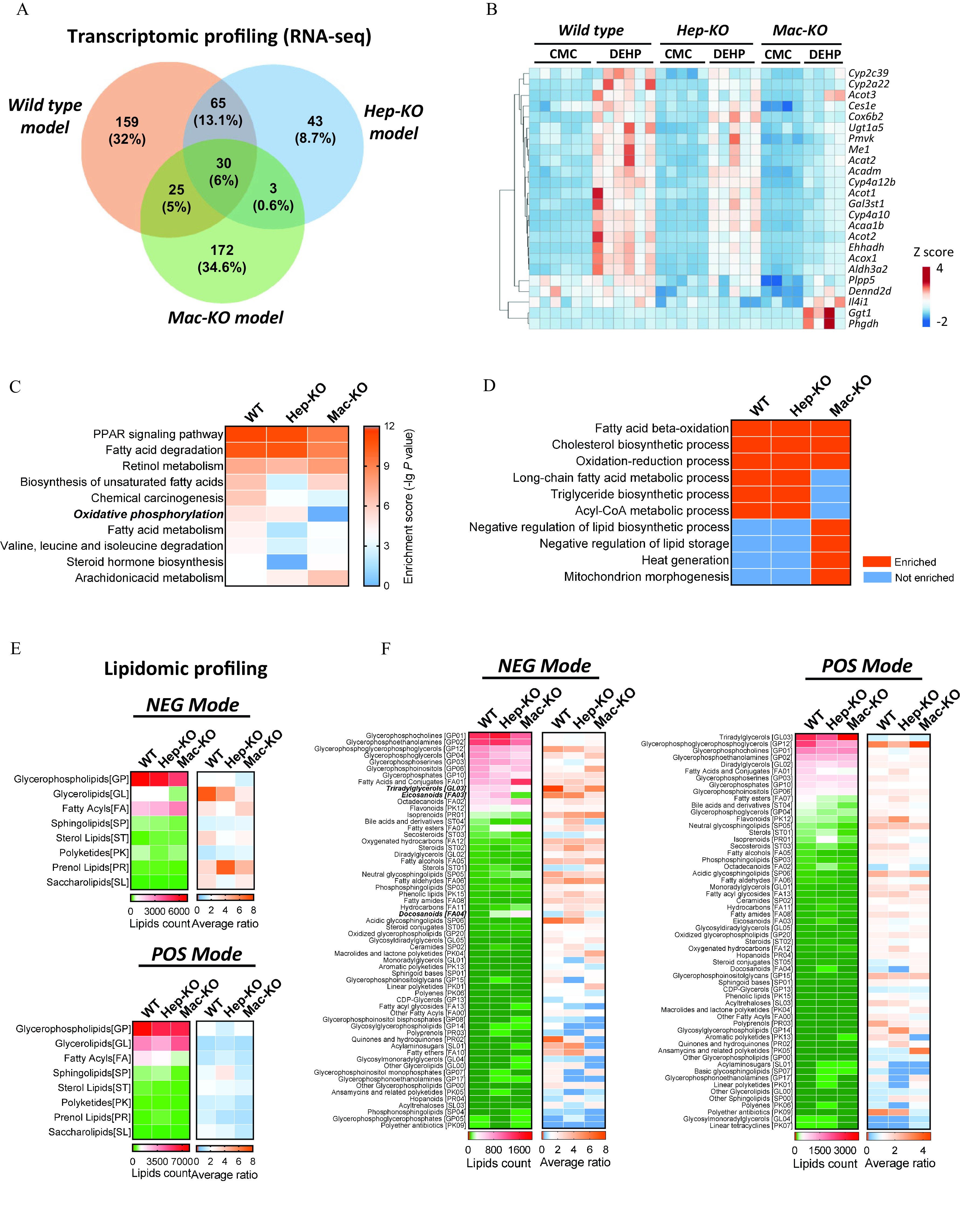
Transcriptomic and lipidomic analysis of DEHP-induced fatty liver. RNA sequencing was performed with the liver of wild-type (WT; ), hepatocyte-specific knockout (Hep-KO; ), and macrophage-specific knockout (Mac-KO; ) mice treated with 0.5% (wt/vol) sodium carboxymethylcellulose (CMC; vehicle control) or DEHP ( BW) by daily gavage for 28 d. (A) Venn diagram of differently expressed genes (DEGs) between DEHP and control (CT) group in the mice models. The data are provided in Table S33. (B) Heatmap of DEGs induced by DEHP in the WT, Hep-KO, and Mac-KO mice models. The data are provided in Table S34. (C) Integrated comparison of pathway enrichment (top 10) across the WT, Hep-KO, and Mac-KO mice models. The data are provided in Table S35. (D) Integrated comparison of Gene Ontology (GO) Biological Process enrichment across the WT, Hep-KO, and Mac-KO mice models. The criteria for “enriched” item is and TOP 20. The data are provided in Table S36. (E) Integrated comparison of DEHP-induced lipidomic changes in the WT, Hep-KO, and Mac-KO mice models. Lipidomic profiling was conducted with the liver of WT (), Hep-KO (), and Mac-KO () mice in the negative ion (NEG) and positive ion (POS) mode. The heatmap shows lipid counts and average fold change (DEHP/CT ratio) of lipid metabolites at the “superclass” level. The data are provided in Table S37. (F) Integrated comparison of DEHP-induced lipidomic changes in the WT, Hep-KO, and Mac-KO mice models at the “class” level. The heatmap shows lipid counts and average fold change in DEHP group compared with the CT group. The data are provided in Table S38. Note: BW, body weight; DEHP, diethylhexyl phthalate; PPAR, peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor.
