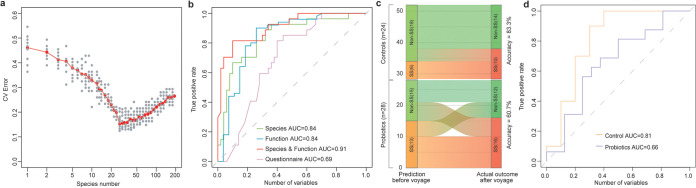
FIG 4.
Random Forest model for predicting the likelihood that crew members would develop seafaring syndrome. (a) Selection of biomarkers based on the gut microbiome for RF model to predict the likelihood of seafaring syndrome developing. The x axis refer to the feature (species) number used in the RF model, and the y axis stands for the error rate of the cross-validation. The relationship between the number of variables in the RF model and model performance were analyzed; 28 biomarkers with the most discriminating power were selected. (b) Prediction performance of RF models using different biomarkers at baseline (e.g.,, only microbial species, only microbial functions, only questionnaire before the voyage, and microbial species plus gene functions), as assessed via the Area Under the Receiver Operating Characteristic Curve (AUC). (c) Comparison of SS prediction result using the microbiome data from day 1 with the actual outcome of SS by questionnaires at the end of the voyage. (d) Performance of SS prediction model for the control and probiotic group of the 30-day voyage.