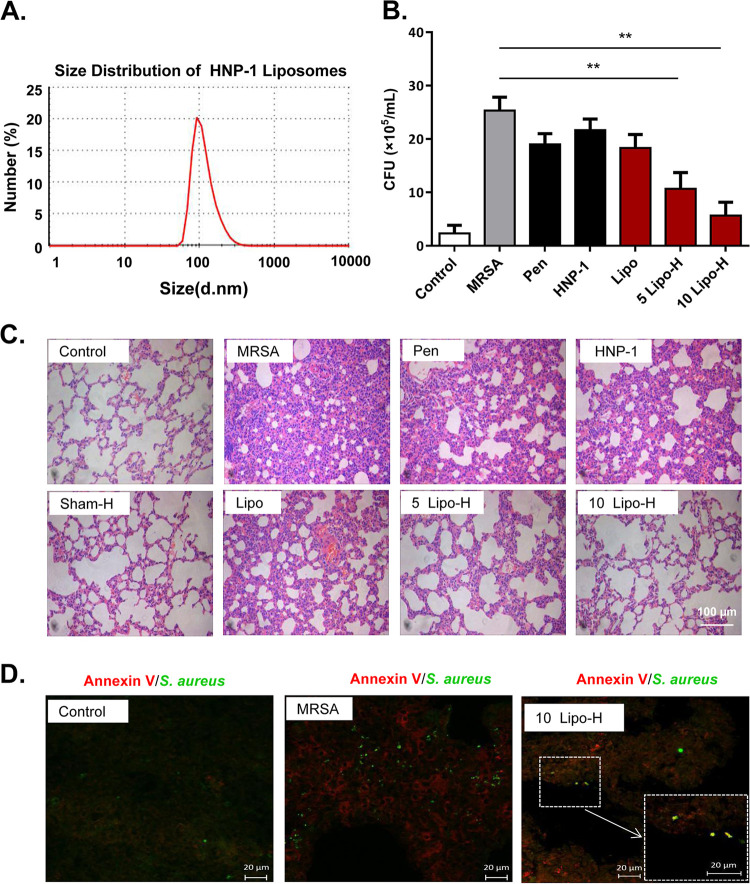
FIG 6.
HNP-1 liposomes attenuated MRSA-induced lung injury in rats. (A) Size distribution of HNP-1 liposomes based on the results from a Zetasizer Nano ZS (Malvern, UK). (B) Comparison of the bacterial counts in the different treatment groups. The number of MRSA isolated from lung lavage fluid were counted on the agar-containing culture plates followed by culturing for 36 h at 37°C. The rats were divided into seven groups: 1) healthy control rats (Control); 2) pneumonic rat models induced by MRSA; 3) 12 μg/ml penicillin treatment as the quality control to ensure the strains are resistant to penicillin (Pen); 4) pneumonic rats treated with 0.1 ml 20 μg/ml HNP-1 solutions (2 μg of HNP-1); 5) pneumonic model rat treated with blank liposomes (Lipo); 6) pneumonic model rats treated with 0.1 ml of 5 μg/ml of liposome-coated HNP-1 (0.5 μg of Lipo-H); and 7) pneumonic model rats treated with 0.1 ml 10 μg/ml liposome-coated HNP-1 (1 μg of Lipo-H). (C) Pathological evaluation via H&E staining in pneumonic model rats. (D) Immunofluorescent staining for Annexin V (red) and S. aureus (green) in pneumonic model rats. Merged images (yellow) indicating of S. aureus apoptosis. Data were analyzed using a two-tailed Student's t test and are plotted as the mean ± SD for each condition. n = 3; *, P < 0.05; and **, P < 0.01.