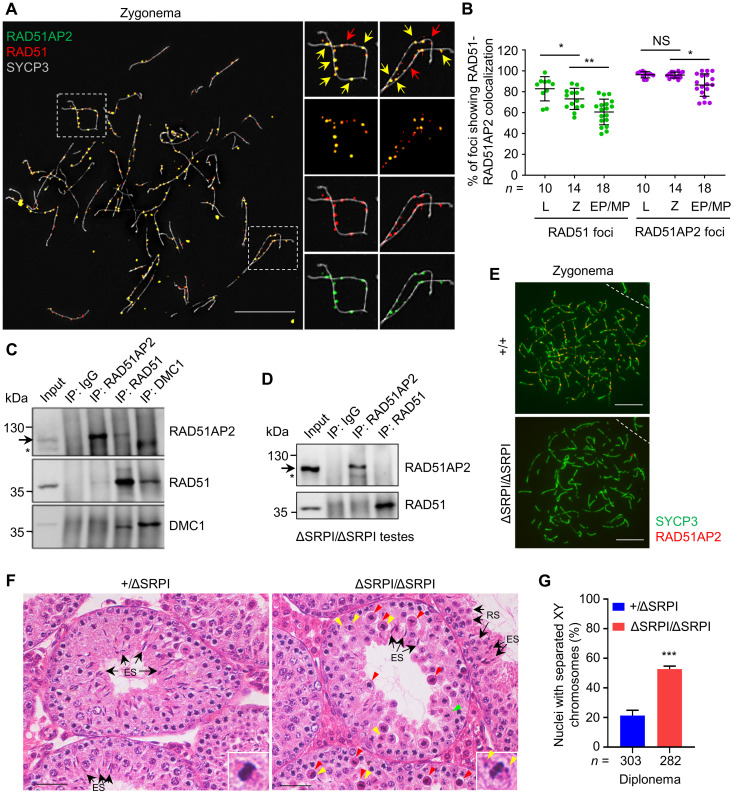
Fig. 6. The RAD51AP2 C terminus mediates the interaction with RAD51 and is essential for RAD51AP2 loading onto chromosome axes.
(A) Representative WT zygotene spread spermatocytes stained for RAD51AP2 (green), RAD51 (red), and SYCP3 (gray) under SIM. Magnified views of the boxed areas are shown on the right. Yellow arrows indicate representative RAD51AP2 foci colocalizing with RAD51. Red arrows indicate representative RAD51 foci existing alone. Scale bars, 10 μm. (B) Ratios of RAD51-RAD51AP2 colocalizing foci to the RAD51 or RAD51AP2 total foci assessed under SIM. n, the number of nuclei scored for each substage. L, leptonema; Z, zygonema. NS, P > 0.05; *P < 0.05; and **P < 0.01, Mann-Whitney U test. (C and D) Co-IP assay with whole-testis extracts of WT (C) and Rad51ap2ΔSRPI/ΔSRPI (D) mice, followed by Western blotting. Arrows indicate the bands corresponding to WT RAD51AP2 proteins (predicted molecular weight, 112.2 kDa) or RAD51AP2 ΔSRPI (predicted molecular weight, 111.7 kDa). Asterisks, a nonspecific band. (E) Representative spread spermatocytes stained for RAD51AP2 (red) and SYCP3 (green). Scale bars, 10 μm. (F) Testicular histology of 6-week-old mice. Green arrowheads, metaphase cells that appear normal. Red arrowheads, metaphase cells with a condensed nucleus indicative of apoptosis. Yellow arrowheads indicate unaligned chromosomes. Arrows indicate representative round spermatids or elongating/elongated spermatids. Scale bars, 50 μm. (G) Frequency of nuclei with XY separation in diplonema. n, the number of cells scored from two mice per genotype. ***P < 0.001, two-tailed Student’s t test.