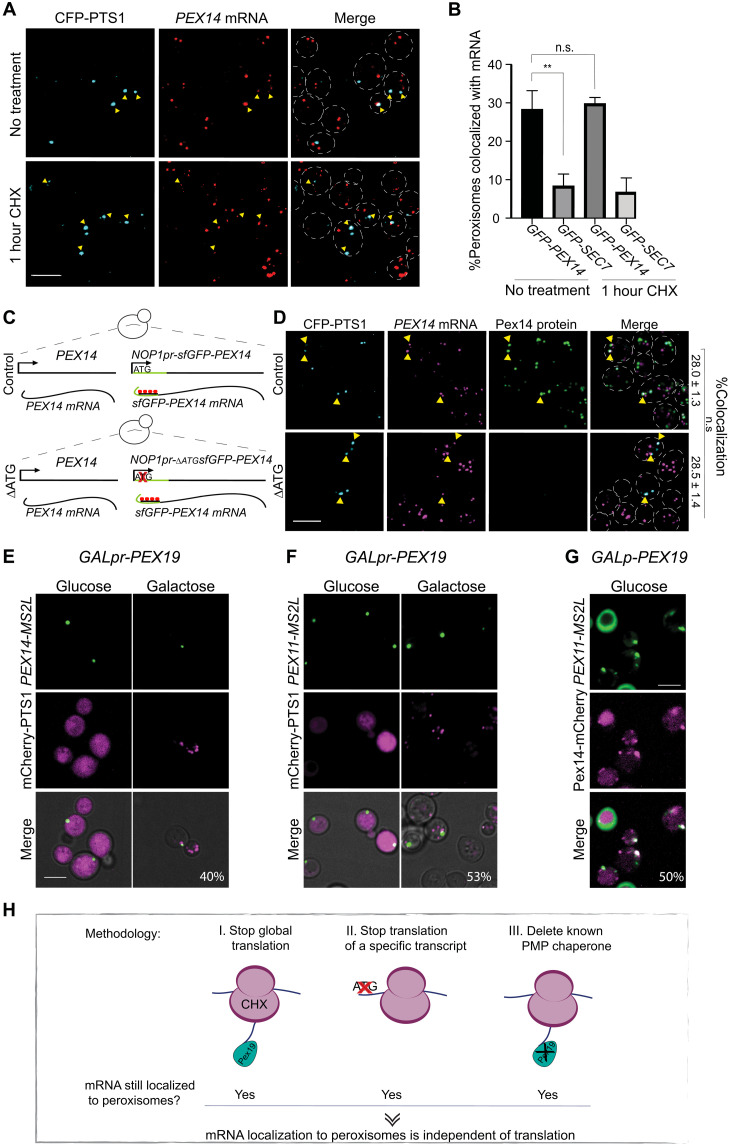
Fig. 1. Peroxisomal mRNA localization is not dependent on translation or Pex19.
(A) Translation inhibition reveals that colocalization of PEX14 mRNA and peroxisomes is translation independent. The maximum intensity projections of confocal images of smRNA-FISH assay of sfGFP-PEX14 (TAMRA, red) following 1-hour incubation with CHX are shown. Peroxisomes in cyan (CFP-PTS1); yellow arrowheads highlight colocalization between PEX14 mRNA and peroxisomes; yeast periphery in dashed white line. (B) Quantification of (A). Random colocalization threshold calculated by mRNA of Golgi SEC7 (n = 150; **P < 0.05, unpaired t test). n.s., not significant. (C) Schematic description of interference with PEX14 translation. sfGFP-PEX14 under the NOP1 promoter (NOP1pr) was integrated into the HO (homothallic switching endonuclease) locus locus either with the start methionine (+ATG) or without (−ATG). (D) Representative smFISH micrographs of +ATG and −ATG strains described above. Mature peroxisomes in cyan (CFP-PTS1), PEX14 mRNA in magenta (TAMRA), and Pex14 protein in green (GFP); yellow arrowheads indicate colocalization. Percentage of peroxisomes colocalizing with sfGFP-PEX14 mRNA (n = 50; P > 0.05, unpaired t test). (E) Representative micrograph from time-lapse experiments of strains following induction of GALpr-PEX19. PEX14-MS2L in green (MS binding coat protein–GFP) and peroxisomes in magenta (mCherry-PTS1). Percentage of mRNA granules colocalizing with peroxisomes. n = 100. (F) Same as (E) but visualizing PEX11-MS2L mRNA (green). (G) Micrograph showing PEX11-MS2L mRNA (green) colocalized with pre-peroxisomal vesicle (PPV) in magenta (Pex14-mCherry) in the absence of Pex19 (GALpr-PEX19 grown on glucose). Percentage of mRNA granules colocalizing with PPVs. Scale bar, 5 μm. (H) Graphical summary of Fig. 1—three experimental methodologies suggest that mRNA localization to peroxisomes is independent of translation.